Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies
- PMID: 17456048
- PMCID: PMC2267306
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20061653
Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies.Biochem J. 2024 Oct 2;481(19):1327. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061653_RET. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 39302111 No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies.Biochem J. 2020 Oct 16;477(19):3897. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061653_EOC. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 33064140 No abstract available.
Abstract
The exposure to non-thermal microwave electromagnetic fields generated by mobile phones affects the expression of many proteins. This effect on transcription and protein stability can be mediated by the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) cascades, which serve as central signalling pathways and govern essentially all stimulated cellular processes. Indeed, long-term exposure of cells to mobile phone irradiation results in the activation of p38 as well as the ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase) MAPKs. In the present study, we have studied the immediate effect of irradiation on the MAPK cascades, and found that ERKs, but not stress-related MAPKs, are rapidly activated in response to various frequencies and intensities. Using signalling inhibitors, we delineated the mechanism that is involved in this activation. We found that the first step is mediated in the plasma membrane by NADH oxidase, which rapidly generates ROS (reactive oxygen species). These ROS then directly stimulate MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases) and allow them to cleave and release Hb-EGF [heparin-binding EGF (epidermal growth factor)]. This secreted factor activates the EGF receptor, which in turn further activates the ERK cascade. Thus this study demonstrates for the first time a detailed molecular mechanism by which electromagnetic irradiation from mobile phones induces the activation of the ERK cascade and thereby induces transcription and other cellular processes.
Figures

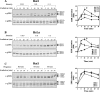
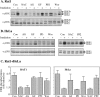
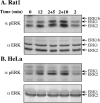
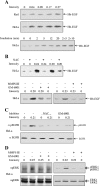

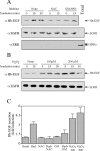
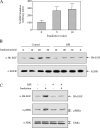
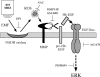
Comment in
-
MAPK activation by radio waves.Biochem J. 2007 Aug 1;405(3):e5-6. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070762. Biochem J. 2007. Retraction in: Biochem J. 2024 Nov 20;481(22):1657. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070762_RET. PMID: 17623008 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Karger C. P. Mobile phones and health: a literature overview. Z. Med. Phys. 2005;15:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Burdalo M., Martin A., Anguiano M., Villar R. On the safety assessment of human exposure in the proximity of cellular communications base-station antennas at 900, 1800 and 2170 MHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005;50:4125–4137. - PubMed
-
- Leszczynski D., Joenvaara S., Reivinen J., Kuokka R. Non-thermal activation of the hsp27/p38MAPK stress pathway by mobile phone radiation in human endothelial cells: molecular mechanism for cancer- and blood-brain barrier-related effects. Differentiation. 2002;70:120–129. - PubMed
-
- Nylund R., Leszczynski D. Proteomics analysis of human endothelial cell line EA.hy926 after exposure to GSM 900 radiation. Proteomics. 2004;4:1359–1365. - PubMed
-
- Weisbrot D., Lin H., Ye L., Blank M., Goodman R. Effects of mobile phone radiation on reproduction and development in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003;89:48–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

