Pathophysiology of sepsis
- PMID: 17456750
- PMCID: PMC1854939
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060872
Pathophysiology of sepsis
Erratum in
- Am J Pathol. 2007 Sep;171(3):1078
Abstract
Sepsis remains a critical problem with significant morbidity and mortality even in the modern era of critical care management. Multiple derangements exist in sepsis involving several different organs and systems, although controversies exist over their individual contribution to the disease process. Septic patients have substantial, life-threatening alterations in their coagulation system, and currently, there is an approved therapy with a component of the coagulation system (activated protein C) to treat patients with severe sepsis. Previously, it was believed that sepsis merely represented an exaggerated, hyperinflammatory response with patients dying from inflammation-induced organ injury. More recent data indicate that substantial heterogeneity exists in septic patients' inflammatory response, with some appearing immuno-stimulated, whereas others appear suppressed. Cellular changes continue the theme of heterogeneity. Some cells work too well such as neutrophils that remain activated for an extended time. Other cellular changes become accelerated in a detrimental fashion including lymphocyte apoptosis. Metabolic changes are clearly present, requiring close and individualized monitoring. At this point in time, the literature richly illustrates that no single mediator/system/pathway/pathogen drives the pathophysiology of sepsis. This review will briefly discuss many of the important alterations that account for the pathophysiology of sepsis.
Figures
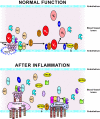
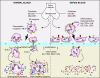
References
-
- Baron RM, Baron MJ, Perrella MA. Pathobiology of sepsis: are we still asking the same questions? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006;34:129–134. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1992;20:864–874. - PubMed
-
- Robertson CM, Coopersmith CM. The systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Microbes Infect. 2006;8:1382–1389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

