Nuclear factor-kappa B, p38, and stress-activated protein kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways regulate proinflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in human placental explants in response to oxidative stress: effects of antioxidant vitamins
- PMID: 17456758
- PMCID: PMC1854947
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.061035
Nuclear factor-kappa B, p38, and stress-activated protein kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways regulate proinflammatory cytokines and apoptosis in human placental explants in response to oxidative stress: effects of antioxidant vitamins
Abstract
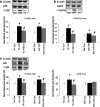
Preeclampsia is a potentially fatal complication of human pregnancy characterized by hypertension, proteinuria, and edema. Placental oxidative stress is a key element in the pathogenesis of the syndrome and results in the release of a cocktail of factors, including proinflammatory cytokines and apoptotic debris, that in turn cause activation of the maternal endothelium. The intermediary molecular mechanisms underlying this release are unknown, but they represent a potential target for therapeutic interventions. We examined activation of signaling pathways during hypoxia-reoxygenation of villous explants in vitro. Hypoxia-reoxygenation activated the p38 and stress-activated protein kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. Downstream consequences included increased tissue concentrations and secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta, increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2, and increased apoptosis. Administration of vitamins C and E to explants blocked activation of the p38 and stress-activated protein kinase MAPK and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. Vitamin administration or p38 pathway inhibition also reduced cyclooxygenase-2 expression, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta secretion, and the levels of apoptosis. We conclude that oxidative stress is a potent inducer of placental synthesis and release of proinflammatory factors. Most of these effects are mediated through the p38 MAPK and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways and can be effectively blocked by vitamins C and E in vitro.
Figures


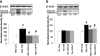

References
-
- Roberts JM, Hubel CA. Is oxidative stress the link in the two-stage model of pre-eclampsia? Lancet. 1999;354:788–789. - PubMed
-
- Redman CW, Sargent IL. Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science. 2005;308:1592–1594. - PubMed
-
- Roberts JM. Endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1998;16:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Burton GJ, Hung T-H. Hypoxia-reoxygenation: a potential source of placental oxidative stress in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. Fetal Maternal Med Rev. 2003;14:97–117.
-
- Brosens JJ, Pijnenborg R, Brosens IA. The myometrial junctional zone spiral arteries in normal and abnormal pregnancies: a review of the literature. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187:1416–1423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

