Early clinical and immune response to NNRTI-based antiretroviral therapy among women with prior exposure to single-dose nevirapine
- PMID: 17457089
- PMCID: PMC2745970
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32810996b2
Early clinical and immune response to NNRTI-based antiretroviral therapy among women with prior exposure to single-dose nevirapine
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether prior exposure to single-dose nevirapine (NVP) for prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission (PMTCT) is associated with attenuated CD4 cell response, death, or clinical treatment failure in women starting antiretroviral therapy (ART) containing non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI).
Methods: Open cohort evaluation of outcomes for women in program sites across Zambia. HIV treatment was provided according to Zambian/World Health Organization guidelines.
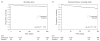
Results: Peripartum NVP exposure status was known for 6740 women initiating NNRTI-containing ART, of whom 751 (11%) reported prior use of NVP for PMTCT. There was no significant difference in mean CD4 cell change between those exposed or unexposed to NVP at 6 (+202 versus +182 cells/microl; P = 0.20) or 12 (+201 versus +211 cells/microl; P = 0.60) months. Multivariable analyses showed no significant differences in mortality [adjusted hazard ratio (HR), 1.2; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.8-1.8] or clinical treatment failure (adjusted HR, 1.1; 95% CI, 0.8-1.5). Comparison of recent NVP exposure with remote exposure suggested a less favorable CD4 cell response at 6 (+150 versus +219 cells/microl; P = 0.06) and 12 (+149 versus +215 cells/microl; P = 0.39) months. Women with recent NVP exposure also had a trend towards elevated risk for clinical treatment failure (adjusted HR, 1.6; 95% CI, 0.9-2.7).
Conclusion: Exposure to maternal single-dose NVP was not associated with substantially different short-term treatment outcomes. However, evidence was suggestive that exposure within 6 months of ART initiation may be a risk factor for poor treatment outcomes, highlighting the importance of ART screening and initiation early in pregnancy.
Figures

References
-
- Jackson JB, Musoke P, Fleming T, Guay LA, Bagenda D, Allen M, et al. Intrapartum and neonatal single-dose nevirapine compared with zidovudine for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Kampala, Uganda: 18-month follow-up of the HIVNET 012 randomised trial. Lancet. 2003;362:859–868. - PubMed
-
- Guay LA, Musoke P, Fleming T, Bagenda D, Allen M, Nakabiito C, et al. Intrapartum and neonatal single-dose nevirapine compared with zidovudine for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Kampala, Uganda: HIVNET 012 randomised trial. Lancet. 1999;354:795–802. - PubMed
-
- Temmerman M, Quaghebeur A, Mwanyumba F, Mandaliya K. Mother-to-child HIV transmission in resource poor settings: how to improve coverage? AIDS. 2003;17:1239–1242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

