Microalbuminuria in HIV infection
- PMID: 17457094
- PMCID: PMC3189480
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3280d3587f
Microalbuminuria in HIV infection
Abstract
Objective: Microalbuminuria is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality. The objective of the study was to evaluate if HIV infection was an independent risk factor for microalbuminuria.
Design: Cross sectional.
Methods: The relationship between HIV infection and microalbuminuria was assessed using subjects enrolled in the study of Fat Redistribution and Metabolic Change in HIV Infection, which consists of HIV-positive and control men and women. Participants with proteinuria (dipstick >or= 1+) were excluded.
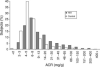
Results: Microalbuminuria (urinary albumin/creatinine ratio, ACR > 30 mg/g) was present in 11% of HIV infected, and 2% of control participants (P < 0.001); a fivefold odds after multivariate adjustment (odds ratio, 5.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.97-13.31; P=0.0008). Several cardiovascular risk factors were associated with higher ACR in HIV participants: insulin resistance (HOMA > 4; 32%, P < 0.0001), systolic blood pressure (21%, P = 0.01 for 120-140 versus < 120 mmHg, and 43%, P = 0.06 for > 140 versus < 120 mmHg), and family history of hypertension (17%, P = 0.03). Higher CD4 cell count was associated with lower albumin/creatinine ratio (-24%, P = 0.009 for 200-400 versus < 200 cells/ml and -26%, P = 0.005 for > 400 versus < 200 cells/ml).
Conclusion: HIV infection had a strong and independent association with microalbuminuria, the severity of which was predicted by markers of insulin resistance, hypertension, and advanced HIV infection. These associations warrant further investigation, as the increased prevalence of microalbuminuria in HIV infection may be a harbinger of future risk of cardiovascular and kidney diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Szczech LA, Gange SJ, van der Horst C, Bartlett JA, Young M, Cohen MH, et al. Predictors of proteinuria and renal failure among women with HIV infection. Kidney Int. 2002;61:195–202. - PubMed
-
- Szczech LA, Hoover DR, Feldman JG, Cohen MH, Gange SJ, Gooze L, et al. The association between renal disease and outcomes among HIV-infected women taking and not taking antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1199–1206. - PubMed
-
- Gardner LI, Klein RS, Szczech LA, Phelps RM, Tashima K, Rompalo AM, et al. Rates and risk factors for overall and specific condition-associated hospitalizations in HIV-infected women. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;34:320–330. - PubMed
-
- Gardner LI, Holmberg SD, Williamson JM, Szczech LA, Carpenter CC, Rompalo AM, et al. Development of proteinuria or elevated serum creatinine and mortality in HIV-infected women. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;32:203–209. - PubMed
-
- Kabanda A, Vandercam B, Bernard A, Lauwerys R, van Ypersele de Strihou C. Low molecular weight proteinuria in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996;27:803–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-HL-74814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI25868/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057508/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI50410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK02724-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-53359/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00636/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073208/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066488-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK002724/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00054/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073208-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-57508/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025868/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials