Cholangiocarcinoma: thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution
- PMID: 17457168
- PMCID: PMC1877058
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000251366.62632.d3
Cholangiocarcinoma: thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution
Abstract
Objective: To assess long-term survival and prognostic factors in a large series of patients with bile duct cancer.
Summary background data: The incidence of bile duct cancer is low but increasing. Determinants of survival vary in the literature, due to a lack of sufficient numbers of patients in most series.
Methods: We studied 564 consecutive patients with bile duct cancer operated upon between 1973 and 2004. Patients were divided into intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal groups. Principle outcome measures were complications, 30-day mortality, and survival.
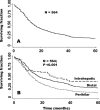
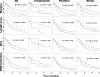
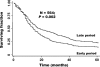
Results: Of the 564 patients, 44 (8%) had intrahepatic, 281 (50%) had perihilar, and 239 (42%) had distal tumors. Approximately half (294, 52%) were treated before 1995, while 270 (48%) were treated thereafter. The perioperative mortality rate was 4%. In log-rank analyses, survival was higher in the later time period (P = 0.002), in patients with intrahepatic disease (P = 0.001), with negative resection margins (P < 0.001), with well/moderately differentiated tumors (P < 0.001), and those with negative lymph nodal status (P < 0.001). In multivariate analysis, negative margins (P < 0.001), tumor differentiation (P < 0.001), and negative nodal status (P < 0.001), but not tumor diameter, were significant independent prognostic factors. In R0-resected patients, lymph node status (P < 0.001), but not tumor diameter, histology, or differentiation, further predicted survival. The median survivals for R0-resected intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal tumors were 80, 30, and 25 months, respectively, and the 5-year survivals were 63%, 30%, and 27%, respectively.
Conclusion: R0 resection remains the best chance for long-term survival, and lymph node status is the most important prognostic factor following R0 resection.
Figures
References
-
- Vauthey JN, Blumgart LH. Recent advances in the management of cholangiocarcinomas. Semin Liver Dis. 1994;14:109–114. - PubMed
-
- Kuwayti K, Baggenstoss AH, Stauffer MH, et al. Carcinoma of the major intrahepatic and the extrahepatic bile ducts exclusive of the papilla of Vater. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1957;104:357–366. - PubMed
-
- Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:115–125. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

