In vivo imaging of changes in tumor oxygenation during growth and after treatment
- PMID: 17457861
- PMCID: PMC2206209
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21212
In vivo imaging of changes in tumor oxygenation during growth and after treatment
Abstract
A novel procedure for in vivo imaging of the oxygen partial pressure (pO2) in implanted tumors is reported. The procedure uses electron paramagnetic resonance imaging (EPRI) of oxygen-sensing nanoprobes embedded in the tumor cells. Unlike existing methods of pO2 quantification, wherein the probes are physically inserted at the time of measurement, the new approach uses cells that are preinternalized (labeled) with the oxygen-sensing probes, which become permanently embedded in the developed tumor. Radiation-induced fibrosarcoma (RIF-1) cells, internalized with nanoprobes of lithium octa-n-butoxy-naphthalocyanine (LiNc-BuO), were allowed to grow as a solid tumor. In vivo imaging of the growing tumor showed a heterogeneous distribution of the spin probe, as well as oxygenation in the tumor volume. The pO2 images obtained after the tumors were exposed to a single dose of 30-Gy X-radiation showed marked redistribution as well as an overall increase in tissue oxygenation, with a maximum increase 6 hr after irradiation. However, larger tumors with a poorly perfused core showed no significant changes in oxygenation. In summary, the use of in vivo EPR technology with embedded oxygen-sensitive nanoprobes enabled noninvasive visualization of dynamic changes in the intracellular pO2 of growing and irradiated tumors.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

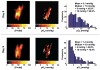

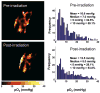


Similar articles
-
Non-invasive measurement of tumor oxygenation using embedded microparticulate EPR spin probe.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2005;566:67-73. doi: 10.1007/0-387-26206-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2005. PMID: 16594136
-
In vivo measurement and imaging of tumor oxygenation using coembedded paramagnetic particulates.Magn Reson Med. 2004 Sep;52(3):650-7. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20188. Magn Reson Med. 2004. PMID: 15334586
-
Novel particulate spin probe for targeted determination of oxygen in cells and tissues.Free Radic Biol Med. 2003 Nov 1;35(9):1138-48. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(03)00496-9. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003. PMID: 14572616
-
Changes of oxygen tension in experimental tumors after a single dose of X-ray irradiation.Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 1;55(11):2249-52. Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 7757972
-
In Vivo pO2 Imaging of Tumors: Oxymetry with Very Low-Frequency Electron Paramagnetic Resonance.Methods Enzymol. 2015;564:501-27. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2015.08.017. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Methods Enzymol. 2015. PMID: 26477263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Tumor Hypoxia In Vivo Using Pattern Recognition of Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI Data.Transl Oncol. 2012 Dec;5(6):437-47. doi: 10.1593/tlo.12319. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Transl Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23326621 Free PMC article.
-
Development of multifunctional Overhauser-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for concurrent in vivo mapping of tumor interstitial oxygenation, acidosis and inorganic phosphate concentration.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 20;9(1):12093. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48524-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31431629 Free PMC article.
-
A paramagnetic implant containing lithium naphthalocyanine microcrystals for high-resolution biological oximetry.J Magn Reson. 2010 Mar;203(1):185-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2009.11.016. Epub 2009 Nov 26. J Magn Reson. 2010. PMID: 20006529 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo photoacoustic lifetime imaging of tumor hypoxia in small animals.J Biomed Opt. 2013 Jul;18(7):076019. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.7.076019. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23877772 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer coating of paramagnetic particulates for in vivo oxygen-sensing applications.Biomed Microdevices. 2009 Apr;11(2):379-87. doi: 10.1007/s10544-008-9244-x. Biomed Microdevices. 2009. PMID: 19083100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okunieff P, Hoeckel M, Dunphy EP, Schlenger K, Knoop C, Vaupel P. Oxygen tension distributions are sufficient to explain the local response of human breast tumors treated with radiation alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993;26:631– 636. - PubMed
-
- Hockel M, Knoop C, Schlenger K, Vorndran B, Baussmann E, Mitze M, Knapstein PG, Vaupel P. Intratumoral pO2 predicts survival in advanced cancer of the uterine cervix. Radiother Oncol. 1993;26:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Brizel DM, Scully SP, Harrelson JM, Layfield LJ, Bean JM, Prosnitz LR, Dewhirst MW. Tumor oxygenation predicts for the likelihood of distant metastases in human soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer Res. 1996;56:941–943. - PubMed
-
- Rofstad EK. Microenvironment-induced cancer metastasis. Int J Radiat Biol. 2000;76:589 – 605. - PubMed
-
- Menon C, Fraker DL. Tumor oxygenation status as a prognostic marker. Cancer Lett. 2005;221:225–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

