T2-prepared SSFP improves diagnostic confidence in edema imaging in acute myocardial infarction compared to turbo spin echo
- PMID: 17457880
- PMCID: PMC2396276
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21215
T2-prepared SSFP improves diagnostic confidence in edema imaging in acute myocardial infarction compared to turbo spin echo
Abstract
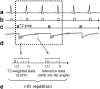
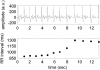
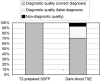
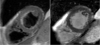
T2-weighted MRI of edema in acute myocardial infarction (MI) provides a means of differentiating acute and chronic MI, and assessing the area at risk of infarction. Conventional T2-weighted imaging of edema uses a turbo spin-echo (TSE) readout with dark-blood preparation. Clinical applications of dark-blood TSE methods can be limited by artifacts such as posterior wall signal loss due to through-plane motion, and bright subendocardial artifacts due to stagnant blood. Single-shot imaging with a T2-prepared SSFP readout provides an alternative to dark-blood TSE and may be conducted during free breathing. We hypothesized that T2-prepared SSFP would be a more reliable method than dark-blood TSE for imaging of edema in patients with MI. In patients with MI (22 acute and nine chronic MI cases), T2-weighted imaging with both methods was performed prior to contrast administration and delayed-enhancement imaging. The T2-weighted images using TSE were nondiagnostic in three of 31 cases, while six additional cases rated as being of diagnostic quality yielded incorrect diagnoses. In all 31 cases the T2-prepared SSFP images were rated as diagnostic quality, correctly differentiated acute or chronic MI, and correctly determined the coronary territory. Free-breathing T2 prepared SSFP provides T2-weighted images of acute MI with fewer artifacts and better diagnostic accuracy than conventional dark-blood TSE.
Published 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Abdel-Aty H, Zagrosek A, Schulz-Menger J, Taylor AJ, Messroghli D, Kumar A, Gross M, Dietz R, Friedrich MG. Delayed enhancement and T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging differentiate acute from chronic myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109:2411–2416. - PubMed
-
- Aletras AH, Tilak GS, Natanzon A, Hsu LY, Gonzalez FM, Hoyt RF, Jr, Arai AE. Retrospective determination of the area at risk for reperfused acute myocardial infarction with T2-weighted cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: histopathological and displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) functional validations. Circulation. 2006;113:1865–1870. - PubMed
-
- Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD, Laub G, Henry DA. “Black blood” T2-weighted inversion-recovery MRI of the heart. Radiology. 1996;199:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Keegan J, Gatehouse PD, Prasad SK, Firmin DN. Improved turbo spinecho imaging of the heart with motion-tracking. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:563–570. - PubMed
-
- Pennell D. Myocardial salvage: retrospection, resolution, and radio waves. Circulation. 2006;113:1821–1823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

