Cadaveric liver transplantation for non-acetaminophen fulminant hepatic failure: a 20-year experience
- PMID: 17457975
- PMCID: PMC4146928
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1427
Cadaveric liver transplantation for non-acetaminophen fulminant hepatic failure: a 20-year experience
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the long-term results of liver transplantation (LT) for non-acetaminophen fulminant hepatic failure (FHF).
Methods: Over a 20-year period, 29 FHF patients underwent cadaveric whole LT. Most frequent causes of FHF were hepatitis B virus and drug-related (not acetaminophen) liver failure. All surviving patients were regularly controlled at the out-patient clinic and none was lost to follow-up. Mean follow-up was 101 mo.
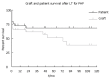
Results: One month, one-, five- and ten-year patient survival was 79%, 72%, 68% and 68%, respectively. One month, one-, five- and ten-year graft survival was 69%, 65%, 51% and 38%, respectively. Six patients needed early (< 2 mo) retransplantation, four for primary non-function, one for early acute refractory rejection because of ABO blood group incompatibility, and one for a malignant tumor found in the donor. Two patients with hepatitis B FHF developed cerebral lesions peri-transplantion: One developed irreversible and extensive brain damage leading to death, and one suffered from deep deficits leading to continuous medical care in a specialized institution.
Conclusion: Long-term outcome of patients transplanted for non-acetaminophen FHF may be excellent. As the quality of life of these patients is also particularly good, LT for FHF is clearly justified, despite lower graft survival compared with LT for other liver diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Detry O, Honoré P, Meurisse M, Jacquet N. Management of fulminant hepatic failure. Acta Chir Belg. 1998;98:235–240. - PubMed
-
- Arkadopoulos N, Detry O, Rozga J, Demetriou AA. Liver assist systems: state of the art. Int J Artif Organs. 1998;21:781–787. - PubMed
-
- Bismuth H, Samuel D, Gugenheim J, Castaing D, Bernuau J, Rueff B, Benhamou JP. Emergency liver transplantation for fulminant hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1987;107:337–341. - PubMed
-
- Barshes NR, Lee TC, Balkrishnan R, Karpen SJ, Carter BA, Goss JA. Risk stratification of adult patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure. Transplantation. 2006;81:195–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials