Beneficial effect of an antibody against interleukin-2 receptor (daclizumab) in an experimental model of hepatocyte xenotransplantation
- PMID: 17457977
- PMCID: PMC4146930
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1435
Beneficial effect of an antibody against interleukin-2 receptor (daclizumab) in an experimental model of hepatocyte xenotransplantation
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the use of Daclizumab (Dmab) as an immunosuppressive agent in an experimental model of hepatocyte xenotransplantation (XenoTx) in rats with fulminant hepatic failure (FHF).
Methods: Two white male New Zealand rabbits were used as donors and 68 Wistar rats as recipients. FHF was induced by intravenous application of dimethylnitrosamine (DMNA). The isolated hepatocytes of the rabbits were xenotransplanted into the spleen of the rats 24 h after FHF induction. Group A (n = 13): no treatment; Group B (n = 14): FHF and XenoTx; Group C (n = 14): FHF and XenoTx and cyclosporin (CsA); Group D (n = 14): FHF and XenoTx and Dmab; Group E (n = 13): FHF and XenoTx and CsA and Dmab. The rats were followed for 15 d.
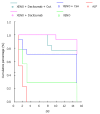
Results: Statistical analysis showed better survival among groups D (92.86%) and E (76.92%) compared to group A (all rats died after 72 h), group B (28.57%) or group C (71.43%), although the differences were not statistically significant. Biochemical evaluation of the liver enzymes and histology confirmed satisfactory function and engraftment, respectively.
Conclusion: This experimental model has shown the safe, effective and beneficial use of Dmab in a xenotransplantation model of rabbit hepatocytes in rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental isolation and transplantation of hepatocytes with the use of antibody against interleukin-2 receptor (daclizumab) as immunosuppressive agent.Transplant Proc. 2005 May;37(4):1929-30. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.02.097. Transplant Proc. 2005. PMID: 15919507
-
Use of mycophenolate mofetil in the experimental allo-transplantation of hepatocytes in rats with fulminant hepatic failure.Transplant Proc. 2004 Jul-Aug;36(6):1739-40. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.06.011. Transplant Proc. 2004. PMID: 15350466
-
Xenotransplantation of hepatocytes in rats with acute liver failure using sirolimus for immunosuppression.J Int Med Res. 2010 Mar-Apr;38(2):546-57. doi: 10.1177/147323001003800217. J Int Med Res. 2010. PMID: 20515568
-
Anti-interleukin-2 receptor antibodies in transplantation: what is the basis for choice?Drugs. 2004;64(16):1737-41. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464160-00001. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15301558 Review.
-
Daclizumab: a review of its use in the prevention of acute rejection in renal transplant recipients.Drugs. 1999 Dec;58(6):1029-42. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199958060-00006. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10651389 Review.
Cited by
-
New Strategies for Acute Liver Failure: Focus on Xenotransplantation Therapy.Cell Med. 2010 Jul 1;1(1):47-54. doi: 10.3727/215517910X516646. eCollection 2010. Cell Med. 2010. PMID: 26998396 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental hepatocyte xenotransplantation--a comprehensive review of the literature.Xenotransplantation. 2015 Jul-Aug;22(4):239-48. doi: 10.1111/xen.12170. Epub 2015 May 7. Xenotransplantation. 2015. PMID: 25950141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leckel K, Blaheta RA, Markus BH. State of hepatocyte transplantation: a risk or a chance? Zentralbl Chir. 2003;128:283–290. - PubMed
-
- Horslen SP, Fox IJ. Hepatocyte transplantation. Transplantation. 2004;77:1481–1486. - PubMed
-
- Papalois A, Arkadopoulos N, Kostopanagiotou G, Theodorakis K, Peveretos P, Golematis B, Papadimitriou J. Experimental xenotransplantation of fresh isolated and cryopreserved pig hepatocytes: a biochemical and morphological study. Transplant Proc. 1997;29:2096–2098. - PubMed
-
- Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, De Groote J, Gudat F, Denk H, Desmet V, Korb G, MacSween RN. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1995;22:696–699. - PubMed
-
- Auchincloss H, Sachs DH. Xenogeneic transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:433–470. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources