KN-93, a specific inhibitor of CaMKII inhibits human hepatic stellate cell proliferation in vitro
- PMID: 17457979
- PMCID: PMC4146932
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1445
KN-93, a specific inhibitor of CaMKII inhibits human hepatic stellate cell proliferation in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of KN-93, a CaMKII selective inhibitor on cell proliferation and the expression of p53 or p21 protein in human hepatic stellate cells.
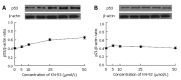
Methods: Human hepatic stellate cells (LX-2) were incubated with various concentrations (0-50 micromol/L) of KN-93 or its inactive derivative, KN-92. Cell proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assay, and the expression of two cell cycle regulators, p53 and p21, was determined by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting.
Results: KN-93 (5-50 micromol/L) decreased the proliferation of human hepatic stellate cells in a dose-dependent manner from 81.76% (81.76% +/- 2.58% vs 96.63% +/- 2.69%, P < 0.05) to 27.15% (27.15% +/- 2.86% vs 96.59% +/- 2.44%, P < 0.01) after 24 h treatment. Incubation of 10 micromol/L KN-93 induced the cell growth reduction in a time-dependent manner from 78.27% at 8 h to 11.48% at 48 h. However, KN-92, an inactive derivative of KN-93, did not inhibit cell proliferation effectively. Moreover, analysis of cell cycle regulator expression revealed that KN-93 rather than KN-92 reduced the expression of p53 and p21.
Conclusion: KN-93 has potent inhibitory effect on proliferation of LX-2 cells by modulating the expression of two special cell cycle regulators, p53 and p21.
Figures


References
-
- Friedman SL, Schiff E, Sorrell M, Maddrey W. Diseases of the Liver. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1998. p. 371–386.
-
- Bissell DM. Hepatic fibrosis as wound repair: a progress report. J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:295–302. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1828–1835. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2247–2250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

