Occludin-mediated premature senescence is a fail-safe mechanism against tumorigenesis in breast carcinoma cells
- PMID: 17459053
- PMCID: PMC11159030
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00494.x
Occludin-mediated premature senescence is a fail-safe mechanism against tumorigenesis in breast carcinoma cells
Abstract
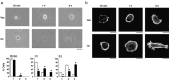
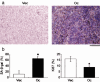
We have previously demonstrated that epigenetic silencing of occludin, a tight junction-associated membrane protein, results in the acquisition of apoptotic resistance to various apoptogenic stimuli, causally contributing to the enhanced tumorigenicity of cancer cells. However, it remains to be examined whether occludin expression in transformed cells has an alternative impact that is important for cancer progression. Here we show that forced expression of occludin induces anoikis and promotes oxidative stress-induced premature senescence in breast carcinoma cells, which is accompanied by upregulation of negative cell cycle regulators such as p16(INK4A), p21(Waf1/Cip1) and p27(Kip1) but not p53. The senescent phenotype is reversed by specific inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Endogenous reexpression of occludin mediated by a synergistic effect with a demethylator and histone deacetylase inhibitor or retinoids that stimulate retinoic acid receptor alpha is also sufficient for provoking the senescent phenotype. In addition, tumors that developed from occludin-expressing cells in mice showed a feature of cellular senescence that has not been described as a consequence of occludin signaling. These findings suggest that the loss of occludin expression is at least partially involved in the senescence-escape program during mammary tumorigenesis.
Figures
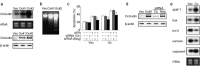


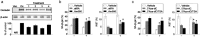
References
-
- Hayflick L, Moorhead PS. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 1961; 25: 585–621. - PubMed
-
- Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME et al . Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a . Cell 1997; 88: 593–602. - PubMed
-
- Campisi J. Cellular senescence as a tumor‐suppressor mechanism. Trends Cell Biol 2001; 11: S27–31. - PubMed
-
- Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Soengas MS et al . BRAFE600‐associated senescence‐like cell cycle arrest of human naevi. Nature 2005; 436: 720–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

