Adiponectin inhibits the growth and peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer through its specific membrane receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2
- PMID: 17459059
- PMCID: PMC11160031
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00486.x
Adiponectin inhibits the growth and peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer through its specific membrane receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2
Abstract
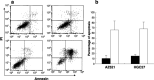
Adiponectin, a circulating peptide hormone produced in adipose tissue, has been shown to be reduced in the plasma of patients with cancer, suggesting that this adipokine may be mechanically involved in the pathogenesis of adiposity-related carcinogenesis. In this study, we examined the expression of adiponectin receptors (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) and assessed the function of adiponectin in gastric cancer. All of the six gastric cancer cell lines significantly expressed mRNA and protein of both receptors with variable levels. Addition of 30 microg/mL adiponectin potently induced apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation of AZ521 and HCG27. Down-regulation of either AdipoR1 or AdipoR2 by specific siRNA significantly suppressed the growth inhibitory effects of adiponectin in both cell lines. Moreover, a local injection of adiponectin markedly inhibited the growth of AZ521 inoculated subcutaneously in nude mice. Similarly, the continuous intraperitoneal infusion of adiponectin effectively suppressed the development of peritoneal metastasis of AZ521. Adiponectin negatively regulates the progression of gastric cancer cells possibly through both AdipoR1 and AdipoR2. Although adiponectin was already reported to have antiangiogenic effects, our results suggest that the antitumor effect of adiponectin was, at least partially, dependent on the direct effects on tumor cells.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Adiponectin receptors are downregulated in human gastric cancer.J Gastroenterol. 2010 Sep;45(9):918-27. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0228-2. Epub 2010 Mar 25. J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20336470
-
Adiponectin receptor-1 expression is associated with good prognosis in gastric cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Nov 11;30(1):107. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-107. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22078265 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of adiponectin and its receptors in rat ovary by human chorionic gonadotrophin treatment and potential involvement of adiponectin in granulosa cell steroidogenesis.Reproduction. 2007 Apr;133(4):719-31. doi: 10.1530/REP-06-0244. Reproduction. 2007. PMID: 17504916
-
Adiponectin and adiponectin receptor in relation to colorectal cancer progression.Int J Cancer. 2010 Dec 15;127(12):2758-67. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25301. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21351255 Clinical Trial.
-
Adiponectin--a key adipokine in the metabolic syndrome.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006 May;8(3):264-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2005.00510.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006. PMID: 16634986 Review.
Cited by
-
Adiponectin and colorectal cancer.Surg Today. 2017 Feb;47(2):151-158. doi: 10.1007/s00595-016-1334-4. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Surg Today. 2017. PMID: 27061803 Review.
-
Overexpression of Adiponectin Receptors in Opium Users with and without Cancer.Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 15;12:59-65. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S256289. eCollection 2020. Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32607004 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and validation of an INflammatory PROtein-driven GAstric cancer Signature (INPROGAS) using antibody microarray-based oncoproteomics.Oncotarget. 2014 Apr 15;5(7):1942-54. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1879. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24722433 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity promotes colonic stem cell expansion during cancer initiation.Cancer Lett. 2015 Dec 28;369(2):336-43. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 26455770 Free PMC article.
-
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae assay system to investigate ligand/AdipoR1 interactions that lead to cellular signaling.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 7;8(6):e65454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065454. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker‐Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1625–38. - PubMed
-
- Carroll KK. Obesity as a risk factor for certain types of cancer. Lipids 1998; 33: 1055–9. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom A, Pisani P, Tenet V, Wolk A, Adami HO. Overweight as an avoidable cause of cancer in Europe. Int J Cancer 2001; 91: 421–30. - PubMed
-
- Peto J. Cancer epidemiology in the last century and the next decade. Nature 2001; 411: 390–5. - PubMed
-
- Cleary MP, Maihle NJ. The role of body mass index in the relative risk of developing premenopausal versus postmenopausal breast cancer. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1997; 216: 28–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

