Soluble Fas ligand inhibits angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17459170
- PMCID: PMC1906820
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2181
Soluble Fas ligand inhibits angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
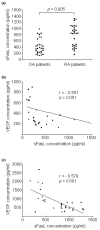
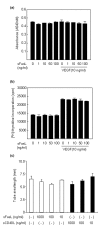
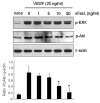
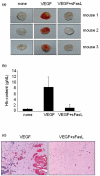
The characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathology include the infiltration of inflammatory leukocytes, the proliferation of synovial cells, and the presence of extensive angiogenesis, referred to as rheumatoid pannus. Fas ligand is critical to the homeostatic regulation of the immune response, but its role in the angiogenic process of RA remains to be defined. In this study, we investigated whether soluble Fas ligand (sFasL) induces synoviocyte apoptosis and regulates angiogenesis of endothelial cells in RA. The levels of sFasL were elevated in the synovial fluids of RA patients when compared to those of osteoarthritis (OA) patients, and they correlated inversely with vascular endothelial growth factor165 (VEGF165) concentrations. sFasL, ranging from 10 to 100 ng/ml, induced the apoptosis of RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) in vitro, and thereby decreased VEGF165 production. In addition, sFasL inhibited VEGF165-induced migration and chemotaxis of endothelial cells to basal levels in a manner independent of the Fas-mediated cell death. sFasL dose-dependently suppressed the VEGF165-stimulated increase in pAkt expression in endothelial cells, which might be associated with its anti-migratory effect on endothelial cells. Moreover, sFasL strongly inhibited neovascularization in the Matrigel plug in vivo. Our data suggest that sFasL shows anti-angiogenic activity within RA joints not only by inducing apoptosis of VEGF165-producing cells but also by blocking VEGF165-induced migration of endothelial cells, independent of Fas-mediated apoptosis.
Figures
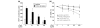

Similar articles
-
Soluble Fas ligand in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Apr;41(4):657-62. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199804)41:4<657::AID-ART12>3.0.CO;2-N. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. PMID: 9550474
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor upregulates angiogenic factors and correlates with clinical measures in rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2007 May;34(5):927-36. Epub 2007 Apr 1. J Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17407222
-
Acute serum amyloid A induces migration, angiogenesis, and inflammation in synovial cells in vitro and in a human rheumatoid arthritis/SCID mouse chimera model.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 1;184(11):6427-37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902941. Epub 2010 Apr 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20435930
-
Growth hormone, VEGF and FGF: involvement in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Chim Acta. 2007 Jan;375(1-2):10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.06.033. Epub 2006 Jul 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2007. PMID: 16893535 Review.
-
Interleukin-18: a mediator of inflammation and angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Oct;31(10):745-51. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0050. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 21864160 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Role of Fas/FasL-Mediated Signal in Peripheral Immune Tolerance.Front Immunol. 2017 Apr 5;8:403. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00403. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28424702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triptolide Modulates TREM-1 Signal Pathway to Inhibit the Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 2;17(4):498. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040498. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27049384 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Triptolide in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Basic Research towards Clinical Translation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 26;19(2):376. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020376. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29373547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis.Autoimmunity. 2009 Nov;42(7):563-73. doi: 10.1080/08916930903143083. Autoimmunity. 2009. PMID: 19863375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of preclinical studies on the efficacy of taurine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Amino Acids. 2021 Jun;53(6):783-800. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-02988-8. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33929638
References
-
- Fearon U, Griosios K, Fraser A, Reece R, Emery P, Jones PF, Veale DJ. Angiopoietins, growth factors, and vascular morphology in early arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:260–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

