Efficient inhibition of HIV-1 expression by LNA modified antisense oligonucleotides and DNAzymes targeted to functionally selected binding sites
- PMID: 17459171
- PMCID: PMC1866241
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-4-29
Efficient inhibition of HIV-1 expression by LNA modified antisense oligonucleotides and DNAzymes targeted to functionally selected binding sites
Abstract
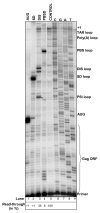
Background: A primary concern when targeting HIV-1 RNA by means of antisense related technologies is the accessibility of the targets. Using a library selection approach to define the most accessible sites for 20-mer oligonucleotides annealing within the highly structured 5'-UTR of the HIV-1 genome we have shown that there are at least four optimal targets available.
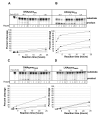
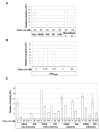
Results: The biological effect of antisense DNA and LNA oligonucleotides, DNA- and LNAzymes targeted to the four most accessible sites was tested for their abilities to block reverse transcription and dimerization of the HIV-1 RNA template in vitro, and to suppress HIV-1 production in cell culture. The neutralization of HIV-1 expression declined in the following order: antisense LNA > LNAzymes > DNAzymes and antisense DNA. The LNA modifications strongly enhanced the in vivo inhibitory activity of all the antisense constructs and some of the DNAzymes. Notably, two of the LNA modified antisense oligonucleotides inhibited HIV-1 production in cell culture very efficiently at concentration as low as 4 nM.
Conclusion: LNAs targeted to experimentally selected binding sites can function as very potent inhibitors of HIV-1 expression in cell culture and may potentially be developed as antiviral drug in patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A genomic selection strategy to identify accessible and dimerization blocking targets in the 5'-UTR of HIV-1 RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Apr 23;32(7):e67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh064. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15107482 Free PMC article.
-
HIV RNA dimerisation interference by antisense oligonucleotides targeted to the 5' UTR structural elements.Virus Res. 2012 Oct;169(1):63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.07.004. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22820401
-
Locked nucleoside analogues expand the potential of DNAzymes to cleave structured RNA targets.BMC Mol Biol. 2006 Jun 5;7:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-7-19. BMC Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16753066 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress in locked nucleic acid research].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2003 Oct;34(4):319-23. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2003. PMID: 14992013 Review. Chinese.
-
LNA-antisense rivals siRNA for gene silencing.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2004 Mar;7(2):188-94. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2004. PMID: 15603252 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges of Assessing Exon 53 Skipping of the Human DMD Transcript with Locked Nucleic Acid-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides in a Mouse Model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2023 Dec;33(6):348-360. doi: 10.1089/nat.2023.0038. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2023. PMID: 38010230 Free PMC article.
-
Locked and unlocked nucleosides in functional nucleic acids.Molecules. 2011 May 27;16(6):4511-26. doi: 10.3390/molecules16064511. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21629180 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of 8,5'-Cyclo 2'-deoxyadenosine on the Activity of 10-23 DNAzyme: Experimental and Theoretical Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 21;25(5):2519. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052519. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473767 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction data of an LNA 7-mer duplex derived from a ricin aptamer.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009 Sep 1;65(Pt 9):881-5. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109029145. Epub 2009 Aug 22. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2009. PMID: 19724123 Free PMC article.
-
Gymnotic Delivery of LNA Mixmers Targeting Viral SREs Induces HIV-1 mRNA Degradation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 3;20(5):1088. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051088. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30832397 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

