Upregulation of polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule in the dorsal hippocampus after contextual fear conditioning is involved in long-term memory formation
- PMID: 17460068
- PMCID: PMC6673006
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0396-07.2007
Upregulation of polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule in the dorsal hippocampus after contextual fear conditioning is involved in long-term memory formation
Abstract
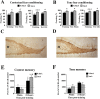
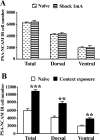
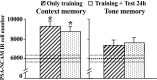
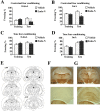
The role of the hippocampus in pavlovian fear conditioning is controversial. Although lesion and pharmacological inactivation studies have suggested a key role for the dorsal hippocampus in contextual fear conditioning, the involvement of the ventral part is still uncertain. Likewise, the debate is open with regard to the putative implication of each hippocampal subdivision in fear conditioning to a discrete conditioned stimulus. We explored the potential existence of dissociations occurring in the dorsal versus ventral hippocampus at the cellular level while dealing with either contextual or cued fear conditioning and focused in a molecular "signature" linked to structural plasticity, the polysialylated form of the neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM). We found an upregulation of PSA-NCAM expression in the dorsal (but not ventral) dentate gyrus at 24 h after contextual (but not tone) fear conditioning. Specific removal of PSA through microinfusion of the enzyme endoneuraminidase-N in the dorsal (but not ventral) hippocampus reduced freezing responses to the conditioned context. Therefore, we present evidence for a specific role of PSA-NCAM in the dorsal hippocampus in the plasticity processes occurring during consolidation of the context representation after "standard" contextual fear conditioning. Interestingly, we also found that exposing animals just to the context induced an activation of PSA-NCAM in both dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus. Altogether, these findings highlighting the distinctive occurrence of these neuroplastic processes in the dorsal hippocampus during the standard contextual fear-conditioning task enlighten the ongoing debate about the involvement of these hippocampal subdivisions in pavlovian fear conditioning.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of hippocampal cell adhesion molecules NCAM and L1 by contextual fear conditioning is dependent upon time and stressor intensity.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Sep;12(9):3283-90. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00191.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10998112
-
Activation of CB1 cannabinoid receptors impairs memory consolidation and hippocampal polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule expression in contextual fear conditioning.Neuroscience. 2009 Feb 18;158(4):1708-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.11.037. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19110037
-
Polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule is involved in induction of long-term potentiation and memory acquisition and consolidation in a fear-conditioning paradigm.J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 18;26(42):10888-109898. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0878-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17050727 Free PMC article.
-
Contextual fear, gestalt memories, and the hippocampus.Behav Brain Res. 2000 Jun 1;110(1-2):73-81. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00186-2. Behav Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 10802305 Review.
-
The hippocampus and contextual memory retrieval in Pavlovian conditioning.Behav Brain Res. 2000 Jun 1;110(1-2):97-108. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00188-6. Behav Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 10802307 Review.
Cited by
-
NCAM function in the adult brain: lessons from mimetic peptides and therapeutic potential.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1163-73. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1007-2. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23494903 Review.
-
Distinct patterns of outcome valuation and amygdala-prefrontal cortex synaptic remodeling in adolescence and adulthood.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 May 7;9:115. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00115. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25999830 Free PMC article.
-
Neural cell adhesion molecule-associated polysialic acid regulates synaptic plasticity and learning by restraining the signaling through GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 17;30(11):4171-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5806-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20237287 Free PMC article.
-
HPA Axis Interactions with Behavioral Systems.Compr Physiol. 2016 Sep 15;6(4):1897-1934. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150042. Compr Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27783863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of Hypothalamus Polysialylation Inducibility Correlates With Maladaptive Eating Behaviors and Predisposition to Obesity.Front Nutr. 2018 Dec 10;5:125. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00125. eCollection 2018. Front Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30619871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Gale GD, Fanselow MS. Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus. 2001;11:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Angata K, Long JM, Bukalo O, Lee W, Dityatev A, Wynshaw-Boris A, Schachner M, Fukuda M, Marth JD. Sialyltransferase ST8Sia-II assembles a subset of polysialic acid that directs hippocampal axonal targeting and promotes fear behaviour. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:32603–32613. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Rawlins JNP, McHugh SB, Deacon RMJ, Yee BK, Bast T, Zhang W-N, Pothuizen HHJ, Feldon J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus—memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2004;28:273–283. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang W-N, Feldon J. The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats: different anterograde amnesias of fear after tetrodotoxin inactivation and infusion of the GABAA agonist muscimol. Exp Brain Res. 2001;139:39–52. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang W-N, Feldon J. Dorsal hippocampus and classical fear conditioning to tone and context in rats: effects of local NMDA-receptor blockade and stimulation. Hippocampus. 2003;13:657–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
