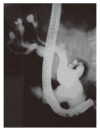
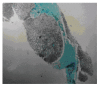
Clinical characteristics of Caroli's syndrome
- PMID: 17461493
- PMCID: PMC4146969
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i13.1934
Clinical characteristics of Caroli's syndrome
Abstract
Caroli's syndrome is characterized by multiple segmental cystic or saccular dilatations of intrahepatic bile ducts associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis. The clinical features of this syndrome reflect both the characteristics of congenital hepatic fibrosis such as portal hypertension and that of Caroli's disease named as recurrent cholangitis and cholelithiasis. The diagnosis depends on both histology and imaging methods which can show the communication between the sacculi and the bile ducts. Treatment consists of symptomatic treatment of cholangitis attacks by antibiotics, some endoscopic, radiological and surgical drainage procedures and surgery. Liver transplantation seems the ultimate treatment for this disease. Prognosis is fairly good unless recurrent cholangitis and renal failure develops.
Figures
References
-
- Sherlock S, Dooley J. Diseases of the liver and billiary system. 11th ed. Milano: Blackwell Sci Pub; 2002. p. 583.
-
- Lu SC, Debian KA. Cystic diseases of the biliary tract. In: Yamada T, Alpers DH, Kaplowitz N, Laine L, Owyang C, et al., editors. Textbook of Gastroenterology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2003. pp. 2225–2233.
-
- Wu KL, Changchien CS, Kuo CM, Chuah SK, Chiu YC, Kuo CH. Caroli's disease - a report of two siblings. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14:1397–1399. - PubMed
-
- Keramidas DC, Kapouleas GP, Sakellaris G. Isolated Caroli's disease presenting as an exophytic mass in the liver. Pediatr Surg Int. 1998;13:177–179. - PubMed
-
- Madjov R, Chervenkov P, Madjova V, Balev B. Caroli's disease. Report of 5 cases and review of literature. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005;52:606–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources