Enhanced therapeutic effects of combined chemotherapeutic drugs and midkine antisense oligonucleotides for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 17461503
- PMCID: PMC4146979
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i13.1989
Enhanced therapeutic effects of combined chemotherapeutic drugs and midkine antisense oligonucleotides for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
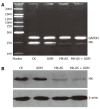
Aim: To evaluate the effect of combined antisense oligonucleotides targeting midkine (MK-AS) and chemotherapeutic drugs [cisplatin(DDP), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and adriamycin (ADM)] on inhibition of HepG2 cell proliferation, and to analyze the efficacy of MK-AS used in combined ADM in in situ human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model.
Methods: HepG2 cells were treated with MK-AS and/or chemotherapeutic drugs mediated by Lipofectin, and cell growth activity was determined by MTS assay. An in situ HCC model was used in this experiment. MK-AS, ADM and MK-AS + ADM were given intravenously for 20 d, respectively. The animal body weight and their tumor weight were measured to assess the effect of the combined therapy in vivo.
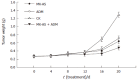
Results: Combined treatment with MK-AS reduced the IC50 of DDP, 5-FU and ADM in HepG2 cells. MK-AS significantly increased the inhibition rate of DDP, 5-FU and ADM. Additionally, synergism (Q 1.15) occurred at a lower concentration of ADM, 5-FU and DDP with combined MK-AS. Combined treatment with MK-AS and ADM resulted in the more growth inhibition on in situ human HCC model compared with treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs alone.
Conclusion: MK-AS increases the chemosensitivity in HepG2 cells and in situ human HCC model, and the combination of MK-AS and ADM has a much better in vitro and in vivo synergism.
Figures



References
-
- Kadomatsu K, Tomomura M, Muramatsu T. cDNA cloning and sequencing of a new gene intensely expressed in early differentiation stages of embryonal carcinoma cells and in mid-gestation period of mouse embryogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;151:1312–1318. - PubMed
-
- Li YS, Milner PG, Chauhan AK, Watson MA, Hoffman RM, Kodner CM, Milbrandt J, Deuel TF. Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated protein that induces mitogenic and neurite outgrowth activity. Science. 1990;250:1690–1694. - PubMed
-
- Merenmies J, Rauvala H. Molecular cloning of the 18-kDa growth-associated protein of developing brain. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:16721–16724. - PubMed
-
- Muramatsu T. Midkine (MK), the product of a retinoic acid responsive gene, and pleiotrophin constitute a new protein family regulating growth and differentiation. Int J Dev Biol. 1993;37:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Minemura M, Tanimura H, Tabor E. Overexpression of multidrug resistance genes MDR1 and cMOAT in human hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatoblastoma cell lines. Int J Oncol. 1999;15:559–563. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

