Selective action of noradrenaline and serotonin on neurones of the spinal superficial dorsal horn in the rat
- PMID: 17463043
- PMCID: PMC2075283
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.131565
Selective action of noradrenaline and serotonin on neurones of the spinal superficial dorsal horn in the rat
Abstract
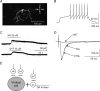
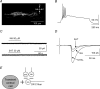
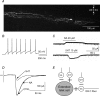
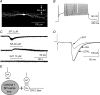
The superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord (SDH; laminae I and II) receives strong input from thin primary afferent fibres and is involved in nociception, pain, temperature sensing and other experiences. The SDH also is the target of serotonergic and adrenergic projections from the brain stem. The interaction between descending pathways that utilize particular mediators and the neurone population of the SDH is poorly understood. To explore this issue, in rat spinal cord slices during whole-cell recordings from identified SDH neurones, noradrenaline (NA) or serotonin (5HT) were briefly applied in the superfusing artificial cerebrospinal fluid. The action of these agents proved specifically related to the type of SDH neurone and its dorsal-root afferent input. Vertical, radial and tonic central lamina II cells consistently expressed outward current to both NA and 5HT, but transient central and Substance P (SP)-insensitive lamina I cells were unaffected directly by either NA or 5HT. Extended islet cells responded with outward current to NA and inward current to 5HT. Lamina I SP-sensitive cells expressed an outward current regularly to NA. 5HT had inhibitory effects on Adelta and C fibre input to all types of SDH neurones. NA inhibited C fibre input to transient central neurones. The present results support the idea that descending systems may have multiple functions, including but not limited to nociceptive modulation.
Figures
References
-
- Aimone LD, Gebhart GF. Spinal monoamine mediation of stimulation-produced antinociception from the lateral hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1987;403:290–300. - PubMed
-
- Aimone LD, Jones SL, Gebhart GF. Stimulation-produced descending inhibition from the periaqueductal gray and nucleus raphe magnus in the rat: mediation by spinal monoamines but not opioids. Pain. 1987;31:123–136. - PubMed
-
- Andrew D, Craig AD. Spinothalamic lamina I neurons selectively sensitive to histamine: a central neural pathway for itch. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:72–77. - PubMed
-
- Baba H, Goldstein PA, Okamoto M, Kohno T, Ataka T, Yoshimura M, Shimoji K. Norepinephrine facilitates inhibitory transmission in substantia gelatinosa of adult rat spinal cord (part 2): effects on somatodendritic sites of GABAergic neurons. Anesthesiology. 2000a;92:485–492. - PubMed
-
- Baba H, Shimoji K, Yoshimura M. Norepinephrine facilitates inhibitory transmission in substantia gelatinosa of adult rat spinal cord (part 1): effects on axon terminals of GABAergic and glycinergic neurons. Anesthesiology. 2000b;92:473–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

