A guanine nucleobase important for catalysis by the VS ribozyme
- PMID: 17464286
- PMCID: PMC1868910
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601698
A guanine nucleobase important for catalysis by the VS ribozyme
Abstract
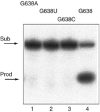
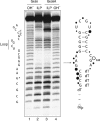
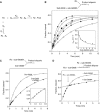
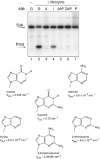
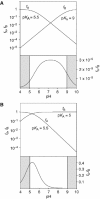
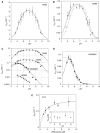
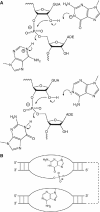
A guanine (G638) within the substrate loop of the VS ribozyme plays a critical role in the cleavage reaction. Replacement by any other nucleotide results in severe impairment of cleavage, yet folding of the substrate is not perturbed, and the variant substrates bind the ribozyme with similar affinity, acting as competitive inhibitors. Functional group substitution shows that the imino proton on the N1 is critical, suggesting a possible role in general acid-base catalysis, and this in accord with the pH dependence of the reaction rate for the natural and modified substrates. We propose a chemical mechanism for the ribozyme that involves general acid-base catalysis by the combination of the nucleobases of guanine 638 and adenine 756. This is closely similar to the probable mechanism of the hairpin ribozyme, and the active site arrangements for the two ribozymes appear topologically equivalent. This has probably arisen by convergent evolution.
Figures
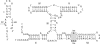
References
-
- Andersen AA, Collins RA (2000) Rearrangement of a stable RNA secondary structure during VS ribozyme catalysis. Mol Cell 5: 469–478 - PubMed
-
- Beaucage SL, Caruthers MH (1981) Deoxynucleoside phosphoramidites—a new class of key intermediates for deoxypolynucleotide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 22: 1859–1862
-
- Bevilacqua PC (2003) Mechanistic considerations for general acid–base catalysis by RNA: revisiting the mechanism of the hairpin ribozyme. Biochemistry 42: 2259–2265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

