Supercritical carbon dioxide: putting the fizz into biomaterials
- PMID: 17464360
- PMCID: PMC1855442
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2005.1687
Supercritical carbon dioxide: putting the fizz into biomaterials
Abstract
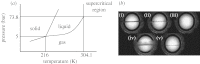
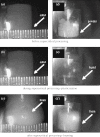
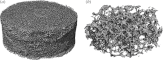
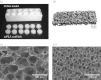
This paper describes recent progress made in the use of high pressure or supercritical fluids to process polymers into three-dimensional tissue engineering scaffolds. Three current examples are highlighted: foaming of acrylates for use in cartilage tissue engineering; plasticization and encapsulation of bioactive species into biodegradable polyesters for bone tissue engineering; and a novel laser sintering process used to fabricate three-dimensional biodegradable polyester structures from particles prepared via a supercritical route.
Figures



References
-
- Alavi S.H., Gogoi B.K., Khan M., Bowman B.J., Rizvi S.S.H.Food Res. Int 321999107–118. 10.1016/S0963-9969(99)00063-0. - DOI
-
- Arora K.A., Lesser A.J., McCarthy T.J.Macromolecules 3119984614–4620. 10.1021/ma971811z. - DOI
-
- Barry J.J.A., Silva M.M.C.G., Shakesheff K.M., Howdle S.M., Alexander M.R.Adv. Funct. Mater 1520051134–1140. 10.1002/adfm.200400562. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
