Erlotinib-associated acute pneumonitis: report of two cases
- PMID: 17464382
- PMCID: PMC2676839
- DOI: 10.1155/2007/832605
Erlotinib-associated acute pneumonitis: report of two cases
Abstract
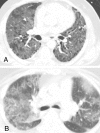
Two cases of erlotinib-associated acute pneumonitis are described. The first patient was started on erlotinib treatment for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. The second patient was treated with erlotinib for metastatic adenocarcinoma of unknown origin. Both patients developed dyspnea and hypoxemia five to six days after initiation of erlotinib treatment. In both cases, computed tomography scan of the chest showed extensive bilateral ground-glass infiltrates consistent with pneumonitis. In both patients, acute pneumonitis resulted in respiratory failure requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage was excluded by bronchoscopy in both cases. Bronchoalveolar lavage cultures were negative. Erlotinib treatment was stopped and both patients were treated with corticosteroids. The first patient improved gradually and finally was discharged to a rehabilitation centre, but unfortunately the second patient died of Klebsiella sepsis. Naranjo causality scale in both cases suggested a probable association between erlotinib and pneumonitis. Literature on erlotinib-associated pneumonitis is sparse. The clinical presentation and radiographic findings of erlotinib-associated acute pneumonitis are described.
On décrit deux cas de pneumonite aiguë associée à l’erlotinib. Le premier patient avait entrepris un traitement à l’erlotinib en raison d’un cancer bronchopulmonaire métastatique non à petites cellules. Le deuxième l’avait commencé en raison d’un adénocarcinome métastatique d’origine inconnue. Les deux patients se sont mis à faire de la dyspnée et de l’hypoxémie de cinq à six jours après le début de ce traitement. Dans les deux cas, la tomodensitométrie du thorax a révélé la présence d’infiltrats bilatéraux étendus « en verre dépoli », compatibles avec une pneumonite, et la pneumonite aiguë a provoqué une insuffisance respiratoire exigeant une intubation et une ventilation mécanique. Chez les deux patients, une bronchoscopie a permis d’écarter la possibilité d’hémorragie alvéolaire diffuse. La culture bronchopulmonaire par lavage était négative. Les deux patients ont abandonné l’erlotinib et entrepris un traitement aux corticoïdes. L’état du premier patient s’est amélioré graduellement, et il a été transféré à un centre de réadaptation. Malheureusement, le second patient est mort d’une septicémie à Klebsiella. Dans les deux cas, l’échelle de causalité de Naranjo laisse supposer une association entre l’erlotinib et la pneumonite. Les publications sont rares au sujet de la pneumonite associée à l’erlotinib. On décrit la présentation clinique et les observations radiographiques de la pneumonite aiguë associée à l’erlotinib.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fatal interstitial lung disease associated with oral erlotinib therapy for lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2007 Aug 5;7:150. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-150. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17683587 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal interstitial lung disease after erlotinib for non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Sep;3(9):1050-3. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318183a9f5. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18758310
-
Independent review of interstitial lung disease associated with death in TRIBUTE (paclitaxel and carboplatin with or without concurrent erlotinib) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2007 Jun;2(6):537-43. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318060d329. J Thorac Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17545850 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety profiles of erlotinib therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011 Jul;11(7):991-7. doi: 10.1586/era.11.74. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21806322 Review.
-
[Hemolytic anemia under erlotinib treatment].Rev Pneumol Clin. 2013 Dec;69(6):345-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pneumo.2013.06.003. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Rev Pneumol Clin. 2013. PMID: 24183296 Review. French.
Cited by
-
New targeted molecular therapies for cancer: radiological response in intrathoracic malignancies and cardiopulmonary toxicity: what the radiologist needs to know.Cancer Imaging. 2014 Jul 23;14(1):26. doi: 10.1186/1470-7330-14-26. Cancer Imaging. 2014. PMID: 25608887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage as a diagnostic procedure: a review of known cellular and molecular findings in various lung diseases.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Sep;12(9):4991-5019. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-651. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 33145073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Nanocochleates Containing Erlotinib HCl and Dexketoprofen Trometamol and Evaluation of In Vitro Characteristic Properties.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2018 Apr;15(1):16-21. doi: 10.4274/tjps.83803. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 32454635 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of Kinase Inhibitors for Treatment of COVID-19.Pharm Res. 2020 Aug 10;37(9):167. doi: 10.1007/s11095-020-02851-7. Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 32778962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of lung-specific toxicity induced by epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncol Lett. 2012 Nov;4(5):865-867. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.872. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23162612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen MH, Johnson JR, Chen YF, Sridhara R, Pazdur R. FDA drug approval summary: Erlotinib (Tarceva) tablets. Oncologist. 2005;10:461–6. - PubMed
-
- Mancuso A, Sternberg CN. New treatments for metastatic kidney cancer. Can J Urol. 2005;12(Suppl 1):66–70. - PubMed
-
- Soulieres D, Senzer NN, Vokes EE, Hidalgo M, Agarwala SS, Siu LL. Multicenter phase II study of erlotinib, an oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent of metastatic squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:77–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical