Is matching innate?
- PMID: 17465311
- PMCID: PMC1832166
- DOI: 10.1901/jeab.2007.92-05
Is matching innate?
Abstract
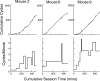
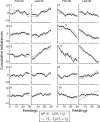
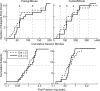
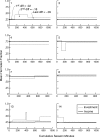
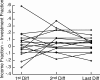
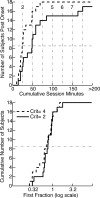
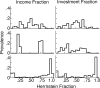
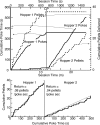
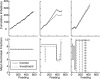
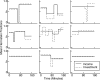
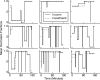
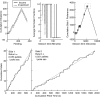
Experimentally naive mice matched the proportions of their temporal investments (visit durations) in two feeding hoppers to the proportions of the food income (pellets per unit session time) derived from them in three experiments that varied the coupling between the behavioral investment and food income, from no coupling to strict coupling. Matching was observed from the outset; it did not improve with training. When the numbers of pellets received were proportional to time invested, investment was unstable, swinging abruptly from sustained, almost complete investment in one hopper, to sustained, almost complete investment in the other-in the absence of appropriate local fluctuations in returns (pellets obtained per time invested). The abruptness of the swings strongly constrains possible models. We suggest that matching reflects an innate (unconditioned) program that matches the ratio of expected visit durations to the ratio between the current estimates of expected incomes. A model that processes the income stream looking for changes in the income and generates discontinuous income estimates when a change is detected is shown to account for salient features of the data.
Figures









References
-
- Balsam P.D, Fairhurst S, Gallistel C.R. Unsignaled unconditioned stimuli degrade contingencies by changing cycle time and temporal uncertainty. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes in press. - PubMed
-
- Belke T.W. Stimulus preference and the transitivity of preference. Animal Learning & Behavior. 1992;20:401–406.
-
- Bush R.R, Mosteller F. A mathematical model for simple learning. Psychological Review. 1951;58:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Church R.M, Guilhardi P. A Turing test of a timing theory. Behavioural Processes. 2005;69:45–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

