Local effects of delayed food
- PMID: 17465314
- PMCID: PMC1832169
- DOI: 10.1901/jeab.2007.13-06
Local effects of delayed food
Abstract
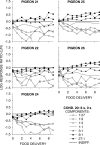
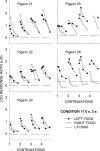
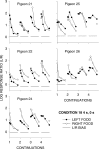
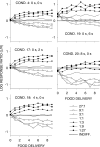
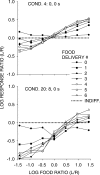
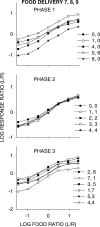
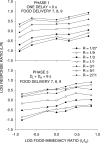
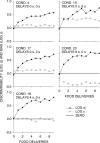
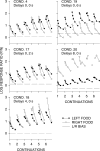
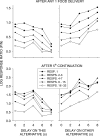
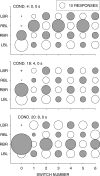
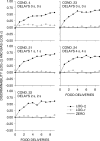
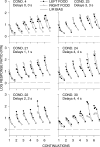
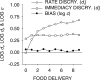
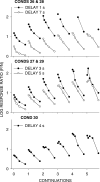
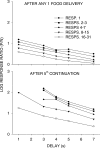
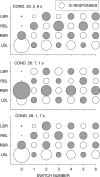
Five pigeons were trained on a procedure in which seven concurrent variable-interval schedules arranged seven different food-rate ratios in random sequence in each session. Each of these components lasted for 10 response-produced food deliveries, and components were separated by 10-s blackouts. We varied delays to food (signaled by blackout) between the two response alternatives in an experiment with three phases: In Phase 1, the delay on one alternative was 0 s, and the other was varied between 0 and 8 s; in Phase 2, both delays were equal and were varied from 0 to 4 s; in Phase 3, the two delays summed to 8 s, and each was varied from 1 to 7 s. The results showed that increasing delay affected local choice, measured by a pulse in preference, in the same way as decreasing magnitude, but we found also that increasing the delay at the other alternative increased local preference. This result casts doubt on the traditional view that a reinforcer strengthens a response depending only on the reinforcer's value discounted by any response-reinforcer delay. The results suggest that food guides, rather than strengthens, behavior.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

