Iron deposition and fat accumulation in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rat
- PMID: 17465448
- PMCID: PMC4319125
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2061
Iron deposition and fat accumulation in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rat
Abstract
Aim: To investigate if iron deposition and fat accumulation in the liver play a pathogenetic role in dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rat.
Methods: Thirty rats were treated with DMN at does consecutive days of 10 microL/kg daily, i.p., for 3 consecutive day each week for 4 wk. Rats (n=30) were sacrificed on the first day (model group A) and 21(st) d (model group B) after cessation of DMN injection. The control group (n=10) received an equivalent amount of saline. Liver tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and Masson and Prussian blue assay and observed under electron microscopy. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and liver tissue hydroxyproline (Hyp) content were tested.
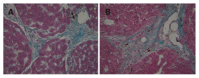
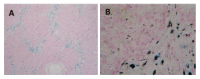
Results: The liver fibrosis did not automatically reverse, which was similar to previous reports, the perilobular deposition of iron accompanied with collagen showed marked characteristics at both the first and 21(st) d after cessation of DMN injection. However, fat accumulation in hepatocytes occurred only at the 21(st) d after cessation of DMN injection.
Conclusion: Iron deposition and fat accumulation may play important roles in pathological changes in DMN-induced rat liver fibrosis. The detailed mechanisms of these characteristics need further research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effects of corydyceps polysaccharide on liver fibrosis induced by DMN in rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006 Dec;31(23):1968-71. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17348192 Chinese.
-
[Inhibitory effects of silymarin on hepatic fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine: experiment with rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Sep 26;86(36):2563-6. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17198567 Chinese.
-
Anti-fibrotic effects of a methylenedioxybenzene compound, CW209292 on dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Aug;32(8):1364-70. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.1364. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19652375
-
[Effect of cordyceps polysaccharide on lipid peroxidation of rats with dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Feb;38(3):391-6. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23668016 Chinese.
-
Dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis and recovery in NOD/SCID mice.J Vet Med Sci. 2011 Jun;73(6):739-45. doi: 10.1292/jvms.10-0311. Epub 2011 Jan 28. J Vet Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21289474
Cited by
-
Supplementation of fresh ucche (Momordica charantia L. var. muricata Willd) prevented oxidative stress, fibrosis and hepatic damage in CCl4 treated rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Apr 11;15:115. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0636-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25884170 Free PMC article.
-
San-Cao Granule () Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis through High Mobility Group Box-1 Protein/Smad Signaling Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2018 Jul;24(7):502-511. doi: 10.1007/s11655-015-2127-0. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Chin J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 26688180
-
In Vivo and In Vitro Models to Study Liver Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Limitations.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;16(3):355-367. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.05.010. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37270060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T 1-T 2 dual-modal magnetic resonance contrast-enhanced imaging for rat liver fibrosis stage.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 14;12(55):35809-35819. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05913d. eCollection 2022 Dec 12. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36545112 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Models and Promising Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies in Liver Fibrosis: An Update.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 11;45(5):4246-4260. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050270. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37232739 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Purohit V, Russo D, Salin M. Role of iron in alcoholic liver disease: introduction and summary of the symposium. Alcohol. 2003;30:93–97. - PubMed
-
- Tung BY, Emond MJ, Bronner MP, Raaka SD, Cotler SJ, Kowdley KV. Hepatitis C, iron status, and disease severity: relationship with HFE mutations. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:318–326. - PubMed
-
- Erhardt A, Maschner-Olberg A, Mellenthin C, Kappert G, Adams O, Donner A, Willers R, Niederau C, Häussinger D. HFE mutations and chronic hepatitis C: H63D and C282Y heterozygosity are independent risk factors for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2003;38:335–342. - PubMed
-
- Powell EE, Jonsson JR, Clouston AD. Steatosis: co-factor in other liver diseases. Hepatology. 2005;42:5–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

