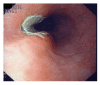
A case of oesophageal ulcer developed after taking homeopathic pill in a young woman
- PMID: 17465462
- PMCID: PMC4319139
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2132
A case of oesophageal ulcer developed after taking homeopathic pill in a young woman
Abstract
Oesophageal ulcers occur mainly as a result of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, pill-induced oesophageal ulcers are a fairly common event. The lesion is mainly due to entrapment of the pill and/or its chemical composition thereof. This case report describes an oesophageal mucosa ulcer occurred in a healthy 35-year old woman who had no previous history of oesophageal disorders and received homeopathic medication. The present case reveals that pill entrapment can occur even in the oesophagus of healthy young individuals and that oesophageal mucosal ulcer can be triggered by substances generally thought devoid of any potentially mucosal aggressive effect.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Etiology, treatment, and outcome of esophageal ulcers: a 10-year experience in an urban emergency hospital.J Gastrointest Surg. 2003 Nov;7(7):836-42. doi: 10.1007/s11605-003-0027-7. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003. PMID: 14592655
-
Case of ulcerative colitis associated with oesophageal ulcer.J Int Med Res. 2000 Jul-Aug;28(4):191-6. doi: 10.1177/147323000002800405. J Int Med Res. 2000. PMID: 11014327
-
Oesophageal ulcers secondary to doxycycline and herpes simplex infection in an immunocompetent patient.Singapore Med J. 2012 Apr;53(4):e69-70. Singapore Med J. 2012. PMID: 22511065
-
Medication-induced oesophageal disorders.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2003 Sep;2(5):495-507. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2.5.495. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2003. PMID: 12946250 Review.
-
Esophageal and Ileal Ulcers Caused by Hydroxycarbamide: A Case Report and Literature Review.Intern Med. 2025 Mar 15;64(6):845-849. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4105-24. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39135249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fatalities after CAM: an overview.Br J Gen Pract. 2011 Jun;61(587):404-5. doi: 10.3399/bjgp11X578070. Br J Gen Pract. 2011. PMID: 21801529 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Simultaneous Esophageal and Gastric Ulceration Due to Doxycycline Ingestion: Case Report and Review of the Literature.Gastroenterology Res. 2012 Dec;5(6):236-238. doi: 10.4021/gr498w. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Gastroenterology Res. 2012. PMID: 27785214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kikendall JW, Johnson LF. Pill-induced esophageal injury. In: The Esophagus., editor. 2nd ed. Castell DO. Boston: Little Brown; 1995. pp. 619–634.
-
- O'Neill JL, Remington TL. Drug-induced esophageal injuries and dysphagia. Ann Pharmacother. 2003;37:1675–1684. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi D, Sugawa C, Shah SH, Tokioka S, Lucas CE. Etiology, treatment, and outcome of esophageal ulcers: a 10-year experience in an urban emergency hospital. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003;7:836–842. - PubMed
-
- Jaspersen D. Drug-induced oesophageal disorders: pathogenesis, incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf. 2000;22:237–249. - PubMed
-
- Kikendall JW. Pill esophagitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999;28:298–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical