Therapeutic and prophylactic thalidomide in TNBS-induced colitis: synergistic effects on TNF-alpha, IL-12 and VEGF production
- PMID: 17465495
- PMCID: PMC4146838
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i15.2166
Therapeutic and prophylactic thalidomide in TNBS-induced colitis: synergistic effects on TNF-alpha, IL-12 and VEGF production
Abstract
Aim: To evaluated the therapeutic and prophylactic effect of thalidomide on 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis. Thalidomide has been reported to downregulate the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), IL-12, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), hallmarks of intestinal inflammation in Crohnos disease (CD).
Methods: Male Wistar rats were divided in five groups of ten animals each. Four groups received a rectal infusion of TNBS in ethanol. The first group was sacrificed 7 d after colitis induction. The second and third groups received either thalidomide or placebo by gavage and were sacrificed at 14 d. The fourth group received thalidomide 6 h before TNBS administration, and was sacrificed 7 d after induction. The fifth group acted as the control group and colitis was not induced. Histological inflammatory scores of the colon were performed and lamina propria CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and VEGF+ cells were detected by immunohistochemistry. TNF-alpha and IL-12 were quantified in the supernatant of organ cultures by ELISA.
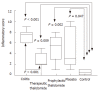
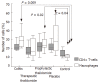
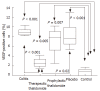
Results: Significant reduction in the inflammatory score and in the percentage of VEGF+ cells was observed in the group treated with thalidomide compared with animals not treated with thalidomide. Both TNF-alpha and IL-12 levels were significantly reduced among TNBS induced colitis animals treated with thalidomide compared with animals that did not receive thalidomide. TNF-alpha levels were also significantly reduced among the animals receiving thalidomide prophylaxis compared with untreated animals with TNBS-induced colitis. Intestinal levels of TNF-alpha and IL-12 were significantly correlated with the inflammatory score and the number of VEGF+ cells.
Conclusion: Thalidomide significantly attenuates TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting the intestinal production of TNF-alpha, IL-12, and VEGF. This effect may support the use of thalidomide as an alternate approach in selected patients with CD.
Figures





References
-
- Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:182–205. - PubMed
-
- Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Papadakis KA, Targan SR. The role of chemokines and chemokine receptors in mucosal inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2000;6:303–313. - PubMed
-
- Reinecker HC, Steffen M, Witthoeft T, Pflueger I, Schreiber S, MacDermott RP, Raedler A. Enhanced secretion of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 beta by isolated lamina propria mononuclear cells from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993;94:174–181. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

