Volitional control of movement: the physiology of free will
- PMID: 17466580
- PMCID: PMC1950571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2007.03.019
Volitional control of movement: the physiology of free will
Abstract
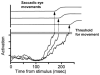
This review deals with the physiology of the initiation of a voluntary movement and the appreciation of whether it is voluntary or not. I argue that free will is not a driving force for movement, but a conscious awareness concerning the nature of the movement. Movement initiation and the perception of willing the movement can be separately manipulated. Movement is generated subconsciously, and the conscious sense of volition comes later, but the exact time of this event is difficult to assess because of the potentially illusory nature of introspection. Neurological disorders of volition are also reviewed. The evidence suggests that movement is initiated in the frontal lobe, particularly the mesial areas, and the sense of volition arises as the result of a corollary discharge likely involving multiple areas with reciprocal connections including those in the parietal lobe and insular cortex.
Figures





References
-
- Aboitiz F, Carrasco X, Schroter C, Zaidel D, Zaidel E, Lavados M. The alien hand syndrome: classification of forms reported and discussion of a new condition. Neurol Sci. 2003;24(4):252–257. - PubMed
-
- Baars BJ. Metaphors of consciousness and attention in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21(2):58–62. - PubMed
-
- Berardelli A, Inghilleri M, Polidori L, Priori A, Mercuri B, Manfredi M. Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on single and sequential arm movements. Exp Brain Res. 1994;98(3):501–506. - PubMed
-
- Berti A, Bottini G, Gandola M, Pia L, Smania N, Stracciari A, et al. Shared cortical anatomy for motor awareness and motor control. Science. 2005;309(5733):488–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

