Temporal and spatial expression of the major allergens in developing and germinating peanut seed
- PMID: 17468222
- PMCID: PMC1914213
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.096933
Temporal and spatial expression of the major allergens in developing and germinating peanut seed
Abstract
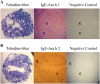
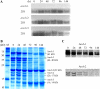
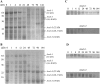
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) seed proteins Ara h 1, Ara h 2, and Ara h 3 are considered to be the major peanut allergens. However, little is known about their temporal and spatial expression during seed development and upon germination and seedling growth. In this study, transcript levels of the three major peanut allergen genes, ara h 1, ara h 2, and ara h 3, and their corresponding proteins were found in all cultivars. Expression patterns were heterogeneous depending on the specific peanut allergen gene and the cultivars tested. However, ara h 3 expression patterns among the cultivars were more variable than ara h 1 and ara h 2. Transcripts were tissue specific, observed in seeds, but not in leaves, flowers, or roots, and were undetectable during seed germination. In situ hybridizations and immunotissue prints revealed that both embryonic axes and cotyledons expressed the allergens. However, more ara h 1 and ara h 3 messenger RNA was detected in cotyledons relative to embryonic axes. Allergen polypeptide degradation patterns were different in embryonic axes compared with cotyledons during germination and seedling growth, with levels of Ara h 1 and Ara h 2 dramatically reduced compared to the Ara h 3 polypeptides in embryonic axes. These characterization studies of major peanut allergen genes and their corresponding seed storage proteins can provide the basic information needed for biochemical and molecular approaches to obtain a hypoallergenic peanut.
Figures

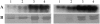




Similar articles
-
Beneficial Influence of Short-Term Germination on Decreasing Allergenicity of Peanut Proteins.J Food Sci. 2016 Jan;81(1):T255-61. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13161. Epub 2015 Nov 30. J Food Sci. 2016. PMID: 26618608
-
Stability of transgene expression in reduced allergen peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) across multiple generations and at different soil sulfur levels.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Feb 18;63(6):1788-97. doi: 10.1021/jf504892f. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25616282
-
Histone deacetylation modification participates in the repression of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seed storage protein gene Ara h 2.02 during germination.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2015 Mar;17(2):522-7. doi: 10.1111/plb.12268. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2015. PMID: 25262939
-
[Progress of researches on the allergens Ara h 1, Ara h 2 and Ara h 3 from peanut].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Dec;27(6):1401-5. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21375004 Review. Chinese.
-
A genetic engineering strategy to eliminate peanut allergy.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005 Jan;5(1):67-73. doi: 10.1007/s11882-005-0058-0. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005. PMID: 15659267 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative and evolutionary analysis of major peanut allergen gene families.Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Sep 4;6(9):2468-88. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu189. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25193311 Free PMC article.
-
Allergenicity reduction of the bio-elicited peanut sprout powder (BPSP) and toxicological acceptance of BPSP-supplemented diets assessed with ICR mice.J Food Sci Technol. 2022 Dec;59(12):4583-4593. doi: 10.1007/s13197-022-05537-7. Epub 2022 Jul 10. J Food Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36276516 Free PMC article.
-
Ethrel-induced release of fresh seed dormancy causes remodelling of amylase activity, proteomics, phytohormone and fatty acid profile of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.).Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2023 Jun;29(6):829-842. doi: 10.1007/s12298-023-01332-6. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2023. PMID: 37520814 Free PMC article.
-
The functional biology of peanut allergens and possible links to their allergenicity.Allergy. 2019 May;74(5):888-898. doi: 10.1111/all.13719. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 30636003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ara h 2 and Ara h 6 have similar allergenic activity and are substantially redundant.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;160(3):251-8. doi: 10.1159/000341642. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23075924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bewley JD, Black M (1994) Seeds: Physiology of Development and Germination, Ed 2. Plenum Press, New York
-
- Boldt A, Fortunato D, Conti A, Petersen A, Ballmer-Weber B, Lepp U, Reese G, Becker WM (2005) Analysis of the composition of an immunoglobulin E reactive high molecular weight protein complex of peanut extract containing Ara h 1 and Ara h 3/4. Proteomics 5 675–686 - PubMed
-
- Burks AW, Cockrell G, Connaughton C, Karpas A, Helm RM (1995. a) Epitope specificity of the major peanut allergen, Ara h II. J Allergy Clin Immunol 95 607–611 - PubMed
-
- Burks AW, Sampson HA, Bannon GA (1998) Review Article Series II. Peanut allergens. Allergy 53 725–730 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

