Asthma exacerbations. 5: assessment and management of severe asthma in adults in hospital
- PMID: 17468458
- PMCID: PMC2117186
- DOI: 10.1136/thx.2005.045203
Asthma exacerbations. 5: assessment and management of severe asthma in adults in hospital
Abstract
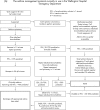
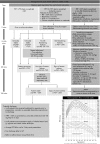
It is difficult to understand why there is such a huge discrepancy between the management of severe asthma recommended by evidence-based guidelines and that observed in clinical practice. The recommendations are relatively straightforward and have been widely promoted both in guidelines and reviews. Specialist physicians need to be more proactive in their implementation of such guidelines through the use of locally derived protocols and assessment sheets, reinforced by audit. The common occurrence of severe asthma and its considerable burden to the community would support such an approach.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Comment in
-
Asthma exacerbations.Thorax. 2008 Jan;63(1):88; author reply 88. Thorax. 2008. PMID: 18156580 No abstract available.
References
-
- British Thoracic Society Guidelines on the management of asthma. Thorax 199348(Suppl 1)S1–24.
-
- British Thoracic Society/Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network British guideline on the management of asthma: a national clinical guideline. Thorax. 2003;58(Suppl I)
-
- Pearson M G, Ryland I, Harrison B D W. Comparison of the process of care of acute severe asthma in adults admitted to hospital before and 1 yr after the publication of national guidelines. Respir Med 199690539–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical