Comparison of indirect assessments of association as predictors of marijuana use among at-risk adolescents
- PMID: 17469944
- PMCID: PMC3134415
- DOI: 10.1037/1064-1297.15.2.218
Comparison of indirect assessments of association as predictors of marijuana use among at-risk adolescents
Abstract
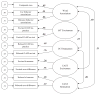
In this study, the authors compared indirect measures that attempt to quantify the level of marijuana associations among adolescents. They also evaluated whether these various methods overlap or tap different aspects of associative processes that may act in concert to influence marijuana use. Automatic drug-relevant associations were assessed in 121 at-risk youth in continuation high schools in California with the use of a word association index and computer-based, reaction time measures (i.e., Implicit Association Test [IAT] and Extrinsic Affective Simon Task [EAST]). Measures of working memory capacity, sensation seeking, and explicit cognitions also were included in analyses as potential confounders. The word association index and the marijuana IAT excited D measure were significant predictors of marijuana use. The word association index accounted for more variance in marijuana use than did the IAT or EAST measures. Further, confirmatory factor analytic models of the indirect measures of marijuana use revealed a significant moderate correlation between the EAST Excitement and Word Association factors but no significant correlations between the Word Association and IAT factors. These findings suggest that there is some convergence among the different indirect measures, but these assessments also appear to tap different aspects of associative processes. The types of indirect measures evaluated in this work provide information about spontaneous cognitions related to substance use, capturing influences on behavior that are not evaluated with traditional explicit assessments of behavior. Findings from this work add to a growing body of research that implicates the importance of implicit associative processes in risk and health behaviors.
Figures

References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 1991.
-
- Ames SL, Stacy AW. Implicit cognition in the prediction of substance use among drug offenders. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors. 1998;12:272–281.
-
- Ames SL, Sussman S, Dent CW, Stacy AW. Implicit cognition and dissocative experiences as predictors of adolescent substance use. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse. 2005;31:129–162. - PubMed
-
- Ames SL, Zogg JB, Stacy AW. Implicit cognition, sensation seeking, marijuana use, and driving behavior among drug offenders. Personality and Individual Differences. 2002;33:1055–1072.
-
- Anderson JR. The architecture of cognition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1983.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

