Calcium-induced folding of a fragment of calmodulin composed of EF-hands 2 and 3
- PMID: 17473011
- PMCID: PMC2206659
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.072777107
Calcium-induced folding of a fragment of calmodulin composed of EF-hands 2 and 3
Abstract
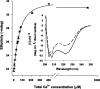
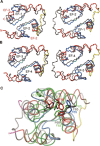
Calmodulin (CaM) is an EF-hand protein composed of two calcium (Ca(2+))-binding EF-hand motifs in its N-domain (EF-1 and EF-2) and two in its C-domain (EF-3 and EF-4). In this study, we examined the structure, dynamics, and Ca(2+)-binding properties of a fragment of CaM containing only EF-2 and EF-3 and the intervening linker sequence (CaM2/3). Based on NMR spectroscopic analyses, Ca(2+)-free CaM2/3 is predominantly unfolded, but upon binding Ca(2+), adopts a monomeric structure composed of two EF-hand motifs bridged by a short antiparallel beta-sheet. Despite having an "even-odd" pairing of EF-hands, the tertiary structure of CaM2/3 is similar to both the "odd-even" paired N- and C-domains of Ca(2+)-ligated CaM, with the conformationally flexible linker sequence adopting the role of an inter-EF-hand loop. However, unlike either CaM domain, CaM2/3 exhibits stepwise Ca(2+) binding with a K (d1) = 30 +/- 5 microM to EF-3, and a K (d2) > 1000 microM to EF-2. Binding of the first equivalent of Ca(2+) induces the cooperative folding of CaM2/3. In the case of native CaM, stacking interactions between four conserved aromatic residues help to hold the first and fourth helices of each EF-hand domain together, while the loop between EF-hands covalently tethers the second and third helices. In contrast, these aromatic residues lie along the second and third helices of CaM2/3, and thus are positioned adjacent to the loop between its "even-odd" paired EF-hands. This nonnative hydrophobic core packing may contribute to the weak Ca(2+) affinity exhibited by EF-2 in the context of CaM2/3.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Peptide binding by a fragment of calmodulin composed of EF-hands 2 and 3.Biochemistry. 2007 Jul 24;46(29):8525-36. doi: 10.1021/bi700265j. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17595060
-
The exchanged EF-hands in calmodulin and troponin C chimeras impair the Ca²⁺-induced hydrophobicity and alter the interaction with Orai1: a spectroscopic, thermodynamic and kinetic study.BMC Biochem. 2015 Feb 15;16:6. doi: 10.1186/s12858-015-0036-7. BMC Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25888318 Free PMC article.
-
A 1.3-A structure of zinc-bound N-terminal domain of calmodulin elucidates potential early ion-binding step.J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 23;374(2):517-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.048. Epub 2007 Sep 21. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17942116 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-Canonical Calmodulin Target Motif Comprising a Polybasic Region and Lipidated Terminal Residue Regulates Localization.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2751. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082751. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obtaining site-specific calcium-binding affinities of calmodulin.Protein Pept Lett. 2003 Aug;10(4):331-45. doi: 10.2174/0929866033478852. Protein Pept Lett. 2003. PMID: 14529487 Review.
Cited by
-
"Iron priming" guides folding of denatured aporubredoxins.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2008 Aug;13(6):981-91. doi: 10.1007/s00775-008-0385-4. Epub 2008 Apr 30. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2008. PMID: 18446387 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-induced changes of the apparent transition-state position in mechanical protein unfolding.Biophys J. 2015 Jul 21;109(2):365-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.009. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26200872 Free PMC article.
-
EF-hand protein, EfhP, specifically binds Ca2+ and mediates Ca2+ regulation of virulence in a human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Sci Rep. 2022 May 25;12(1):8791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12584-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35614085 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-dependent folding of single calmodulin molecules.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 30;109(44):17814-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201801109. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22753517 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin: The switch button of calcium signaling.Tzu Chi Med J. 2021 Aug 23;34(1):15-22. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_285_20. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021. PMID: 35233351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andre I. and Linse, S. 2002. Measurement of Ca2+-binding constants of proteins and presentation of the CaLigator software. Anal. Biochem. 305: 195–205. - PubMed
-
- Babu Y.S., Bugg, C.E., and Cook, W.J. 1988. Structure of calmodulin refined at 2.2 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 204: 191–204. - PubMed
-
- Biekofsky R.R., Martin, S.R., Browne, J.P., Bayley, P.M., and Feeney, J. 1998. Ca2+ coordination to backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms in calmodulin and other EF-hand proteins: 15N chemical shifts as probes for monitoring individual-site Ca2+ coordination. Biochemistry 37: 7617–7629. - PubMed
-
- Brent R. 1998. Protein expression. In Current protocols in molecular biology (eds. F. Ausubel et al.), pp. 16.10.11–16.21.19. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
-
- Brunger A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54: 905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

