A fluorescence polarization-based screening assay for nucleic acid polymerase elongation activity
- PMID: 17475199
- PMCID: PMC2713175
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.03.039
A fluorescence polarization-based screening assay for nucleic acid polymerase elongation activity
Abstract
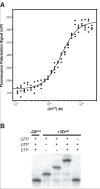
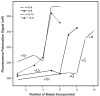
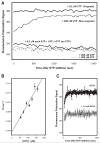
We have devised a simple high-throughput screening compatible fluorescence polarization-based assay that can be used to detect the elongation activity of nucleic acid polymerase enzymes. The assay uses a 5' end-labeled template strand and relies on an increase in the polarization signal from the fluorescent label as it is drawn in toward the active site by the action of the enzyme. If the oligonucleotide is sufficiently short, the fluorescence polarization signal can also be used to detect binding prior to elongation activity. We refer to the nucleic acid substrate as a polymerase elongation template element (PETE) and demonstrate the utility of this PETE assay in a microtiter plate format using the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from poliovirus to extend a self-priming hairpin RNA. The PETE assay provides an efficient method for screening compounds that may inhibit the nucleic acid binding or elongation activities of polymerases.
Figures

References
-
- Beaulieu PL. Finger loop inhibitors of the HCV NS5B polymerase: discovery and prospects for new HCV therapy. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2006;9:618–26. - PubMed
-
- Arnold JJ, Cameron CE. Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (3D(pol)). Assembly of stable, elongation-competent complexes by using a symmetrical primer-template substrate (sym/sub) J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5329–36. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer-Orta C, Arias A, Perez-Luque R, Escarmis C, Domingo E, Verdaguer N. Structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and its complex with a template-primer RNA. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47212–21. - PubMed
-
- Yin YW, Steitz TA. Structural basis for the transition from initiation to elongation transcription in T7 RNA polymerase. Science. 2002;298:1387–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

