Novel strategy for treatment of viral central nervous system infection by using a cell-permeating inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- PMID: 17475657
- PMCID: PMC1933289
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00467-07
Novel strategy for treatment of viral central nervous system infection by using a cell-permeating inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase
Abstract
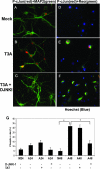
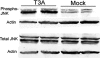
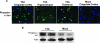
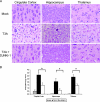
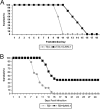
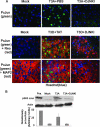
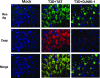
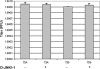
Viral encephalitis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, yet there is no proven efficacious therapy for most viral infections of the central nervous system (CNS). Many of the viruses that cause encephalitis induce apoptosis and activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) following infection. We have previously shown that reovirus infection of epithelial cell lines activates JNK-dependent apoptosis. We now show that reovirus infection resulted in activation of JNK and caspase-3 in the CNS. Treatment of reovirus-infected mice with a cell-permeating peptide that competitively inhibits JNK activity resulted in significantly prolonged survival of intracerebrally infected mice following an otherwise lethal challenge with T3D (100 x 50% lethal dose). Protection correlated with reduced CNS injury, reduced neuronal apoptosis, and reduced c-Jun activation without altering the viral titer or viral antigen distribution. Given the efficacy of the inhibitor in protecting mice from viral encephalitis, JNK inhibition represents a promising and novel treatment strategy for viral encephalitis.
Figures
References
-
- Barr, R. K., T. S. Kendrick, and M. A. Bogoyevitch. 2002. Identification of the critical features of a small peptide inhibitor of JNK activity. J. Biol. Chem. 277:10987-10997. - PubMed
-
- Bonny, C., A. Oberson, S. Negri, C. Sauser, and D. F. Schorderet. 2001. Cell-permeable peptide inhibitors of JNK: novel blockers of beta-cell death. Diabetes 50:77-82. - PubMed
-
- Borsello, T., P. G. Clarke, L. Hirt, A. Vercelli, M. Repici, D. F. Schorderet, J. Bogousslavsky, and C. Bonny. 2003. A peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase protects against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia. Nat. Med. 9:1180-1186. - PubMed
-
- Borsello, T., K. Croquelois, J. P. Hornung, and P. G. Clarke. 2003. N-methyl-d-aspartate-triggered neuronal death in organotypic hippocampal cultures is endocytic, autophagic and mediated by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 18:473-485. - PubMed
-
- Chang, L., Y. Jones, M. H. Ellisman, L. S. Goldstein, and M. Karin. 2003. JNK1 is required for maintenance of neuronal microtubules and controls phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins. Dev. Cell 4:521-533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

