New transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein isoform, gamma-7, differentially regulates AMPA receptors
- PMID: 17475805
- PMCID: PMC6672084
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5561-06.2007
New transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein isoform, gamma-7, differentially regulates AMPA receptors
Abstract
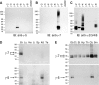
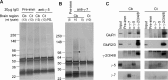
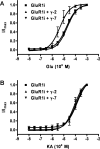
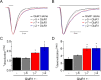
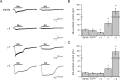
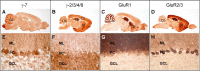
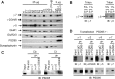
AMPA-type glutamate receptors (GluRs) mediate most excitatory signaling in the brain and are composed of GluR principal subunits and transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein (TARP) auxiliary subunits. Previous studies identified four mammalian TARPs, gamma-2 (or stargazin), gamma-3, gamma-4, and gamma-8, that control AMPA receptor trafficking, gating, and pharmacology. Here, we explore roles for the homologous gamma-5 and gamma-7 proteins, which were previously suggested not to serve as TARPs. Western blotting reveals high levels of gamma-5 and gamma-7 in the cerebellum, where gamma-7 is enriched in Purkinje neurons in the molecular layer and glomerular synapses in the granule cell layer. Immunoprecipitation proteomics shows that cerebellar gamma-7 avidly and selectively binds to AMPA receptor GluR subunits and also binds to the AMPA receptor clustering protein, postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95). Furthermore, gamma-7 occurs together with PSD-95 and AMPA receptor subunits in purified postsynaptic densities. In heterologous cells, gamma-7 but not gamma-5 greatly enhances AMPA receptor glutamate-evoked currents and modulates channel gating. In granule cells from stargazer mice, transfection of gamma-7 but not gamma-5 increases AMPA receptor-mediated currents. Compared with stargazin, gamma-7 differentially modulates AMPA receptor glutamate affinity and kainate efficacy. These studies define gamma-7 as a new member of the TARP family that can differentially influence AMPA receptors in cerebellar neurons.
Figures

References
-
- Allen Institute for Brain Science. Allen Brain Atlas. 2007. Retrieved April 18, 2007, from: http://www.brainmap.org.
-
- Bedoukian MA, Weeks AM, Partin KM. Different domains of the AMPA receptor direct stargazin-mediated trafficking and stargazin-mediated modulation of kinetics. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:23908–23921. - PubMed
-
- Burgess DL, Gefrides LA, Foreman PJ, Noebels JL. A cluster of three novel Ca2+ channel gamma subunit genes on chromosome 19q13.4: evolution and expression profile of the gamma subunit gene family. Genomics. 2001;71:339–350. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, El-Husseini A, Tomita S, Bredt DS, Nicoll RA. Stargazin differentially controls the trafficking of alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate and kainate receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64:703–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
