Sensorimotor gating in larval zebrafish
- PMID: 17475807
- PMCID: PMC6672105
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0615-07.2007
Sensorimotor gating in larval zebrafish
Abstract
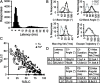
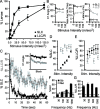
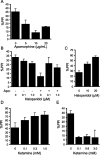
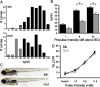
Control of behavior in the natural environment where sensory stimuli are abundant requires superfluous information to be ignored. In part, this is achieved through selective transmission, or gating of signals to motor systems. A quantitative and clinically important measure of sensorimotor gating is prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the startle response, impairments in which have been demonstrated in several neuropsychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia. Here, we show for the first time that the acoustic startle response in zebrafish larvae is modulated by weak prepulses in a manner similar to mammalian PPI. We demonstrate that, like in mammals, antipsychotic drugs can suppress disruptions in zebrafish PPI induced by dopamine agonists. Because genetic factors underlying PPI are not well understood, we performed a screen and isolated mutant lines with reduced PPI. Analysis of Ophelia mutants demonstrates that they have normal sensory acuity and startle performance, but reduced PPI, suggesting that Ophelia is critical for central processing of sensory information. Thus, our results provide the first evidence for sensorimotor gating in larval zebrafish and report on the first unbiased screen to identify genes regulating this process.
Figures



References
-
- Abel KM, Allin MP, Hemsley DR, Geyer MA. Low dose ketamine increases prepulse inhibition in healthy men. Neuropharmacology. 2003;44:729–737. - PubMed
-
- Anholt RR, Mackay TF. Quantitative genetic analyses of complex behaviours in Drosophila. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:838–849. - PubMed
-
- Anokhin AP, Heath AC, Myers E, Ralano A, Wood S. Genetic influences on prepulse inhibition of startle reflex in humans. Neurosci Lett. 2003;353:45–48. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal TD, Goode CT. The startle eyeblink response to low intensity acoustic stimuli. Psychophysiology. 1991;28:296–306. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal TD, Elden A, Flaten MA. A comparison of several methods used to quantify prepulse inhibition of eyeblink responding. Psychophysiology. 2004;41:326–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
