Polo-like kinase controls vertebrate spindle elongation and cytokinesis
- PMID: 17476331
- PMCID: PMC1853238
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000409
Polo-like kinase controls vertebrate spindle elongation and cytokinesis
Abstract
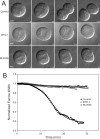
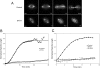
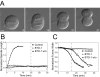
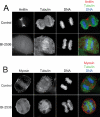
During cell division, chromosome segregation must be coordinated with cell cleavage so that cytokinesis occurs after chromosomes have been safely distributed to each spindle pole. Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is an essential kinase that regulates spindle assembly, mitotic entry and chromosome segregation, but because of its many mitotic roles it has been difficult to specifically study its post-anaphase functions. Here we use small molecule inhibitors to block Plk1 activity at anaphase onset, and demonstrate that Plk1 controls both spindle elongation and cytokinesis. Plk1 inhibition did not affect anaphase A chromosome to pole movement, but blocked anaphase B spindle elongation. Plk1-inhibited cells failed to assemble a contractile ring and contract the cleavage furrow due to a defect in Rho and Rho-GEF localization to the division site. Our results demonstrate that Plk1 coordinates chromosome segregation with cytokinesis through its dual control of anaphase B and contractile ring assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Eggert US, Mitchison TJ, Field CM. Animal cytokinesis: from parts list to mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:543–566. - PubMed
-
- Maiato H, DeLuca J, Salmon ED, Earnshaw WC. The dynamic kinetochore-microtubule interface. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:5461–5477. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Sillje HH, Nigg EA. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Sumara I, Gimenez-Abian JF, Gerlich D, Hirota T, Kraft C, et al. Roles of polo-like kinase 1 in the assembly of functional mitotic spindles. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1712–1722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

