Rickettsia parkeri infection after tick bite, Virginia
- PMID: 17479907
- PMCID: PMC2725880
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1302.061295
Rickettsia parkeri infection after tick bite, Virginia
Abstract
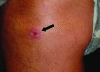
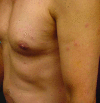
We describe a man with a febrile illness and an eschar that developed at the site of a tick bite. Rickettsia parkeri was detected and isolated from the eschar. This report represents the second documented case of R. parkeri rickettsiosis in a US serviceman in eastern Virginia.
Figures
References
-
- Parker RR, Hohls GM, Cox GW, Davis GE. Observations on an infectious agent from Amblyomma maculatum. Public Health Rep. 1939;54:1482–4.
-
- Jiang J, Chan TC, Temenak JJ, Dasch GA, Ching WM, Richards AL. Development of a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay specific for Orientia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:351–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical