Glutamate signaling proteins and tyrosine hydroxylase in the locus coeruleus of alcoholics
- PMID: 17481661
- PMCID: PMC2292639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.02.010
Glutamate signaling proteins and tyrosine hydroxylase in the locus coeruleus of alcoholics
Abstract
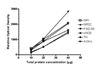
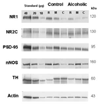
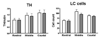
It has been postulated that alcoholism is associated with abnormalities in glutamatergic neurotransmission. This study examined the density of glutamate NMDA receptor subunits and its associated proteins in the noradrenergic locus coeruleus (LC) in deceased alcoholic subjects. Our previous research indicated that the NMDA receptor in the human LC is composed of obligatory NR1 and regulatory NR2C subunits. At synapses, NMDA receptors are stabilized through interactions with postsynaptic density protein (PSD-95). PSD-95 provides structural and functional coupling of the NMDA receptor with neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), an intracellular mediator of NMDA receptor activation. LC tissue was obtained from 10 alcohol-dependent subjects and eight psychiatrically healthy controls. Concentrations of NR1 and NR2C subunits, as well as PSD-95 and nNOS, were measured using Western blotting. In addition, we have examined tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of norepinephrine. The amount of NR1 was lower in the rostral (-30%) and middle (-41%) portions of the LC of alcoholics as compared to control subjects. No differences in the amounts of NR2C, PSD-95, nNOS and TH were detected comparing alcoholic to control subjects. Lower levels of NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptor in the LC implicates altered glutamate-norepinephrine interactions in alcoholism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduced levels of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptor and PSD-95 in the prefrontal cortex in major depression.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Feb 1;33(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 18992785 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of NR2A and PSD-95 in the lateral amygdala in depression.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009 Mar;12(2):143-53. doi: 10.1017/S1461145708008985. Epub 2008 Jun 23. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18570704 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of the NR2C subunit of the NMDA receptor in the locus coeruleus in depression.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Aug;30(8):1557-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300781. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15920498 Free PMC article.
-
The subcellular distribution of nitric oxide synthase relative to the NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors in the cerebral cortex.Prog Brain Res. 1998;118:83-97. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63202-1. Prog Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9932436 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of the locus coeruleus in suicide.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997 Dec 29;836:233-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb52363.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997. PMID: 9616802 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced levels of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptor and PSD-95 in the prefrontal cortex in major depression.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Feb 1;33(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 18992785 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and affective disorders.IBRO Rep. 2018 Nov 17;5:116-132. doi: 10.1016/j.ibror.2018.11.004. eCollection 2018 Dec. IBRO Rep. 2018. PMID: 30591953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Markers of apoptosis induction and proliferation in the orbitofrontal cortex in alcohol dependence.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Nov;38(11):2790-9. doi: 10.1111/acer.12559. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 25421516 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of NR2A and PSD-95 in the lateral amygdala in depression.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009 Mar;12(2):143-53. doi: 10.1017/S1461145708008985. Epub 2008 Jun 23. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18570704 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate receptor subunit expression in the rhesus macaque locus coeruleus.Brain Res. 2007 Oct 10;1173:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.08.007. Epub 2007 Aug 9. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17765206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alele PE, Devaud LL. Differential adaptations in GABAergic and glutamatergic systems during ethanol withdrawal in male and female rats. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2005;29:1027–1034. - PubMed
-
- Arango V, Underwood MD, Mann JJ. Fewer pigmented neurons in the locus coeruleus of uncomplicated alcoholics. Brain Research. 1994;650:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Foote SL, Bloom FE. Low doses of ethanol disrupt sensory responses of brain noradrenergic neurones. Nature. 1982;296:857–860. - PubMed
-
- Aston-Jones G, Shipley MT, Chouvet G, Ennis M, van Bockstaele E, Pieribone V, Shiekhattar R, Akaoka H, Drolet G, Astier B, et al. Afferent regulation of locus coeruleus neurons: anatomy, physiology and pharmacology. Progress in Brain Research. 1991;88:47–75. - PubMed
-
- Baker KG, Halliday GM, Harper CG. Effect of chronic alcohol consumption on the human locus coeruleus. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1994;18:1491–1496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

