Visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in a subset of rats following TNBS-induced colitis
- PMID: 17481818
- PMCID: PMC2807887
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.03.029
Visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in a subset of rats following TNBS-induced colitis
Abstract
Background: Chronic abdominal pain is one of the most common gastrointestinal symptoms experienced by patients. Visceral hypersensitivity has been shown to be a biological marker in many patients with chronic visceral pain. We have previously shown that IBS patients with visceral hypersensitivity also have evidence of thermal hyperalgesia of the hand/foot.
Objective: The objective of the current study was to develop an animal model of chronic visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in rats treated with intracolonic trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.
Design: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200-250g) were treated with either 20mg/rat trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS, Sigma Chemical Co.) in 50% ethanol (n=75), an equivalent volume of 50% ethanol (n=20) or an equivalent volume of saline (n=20). The agents were delivered with a 24-gauge catheter inserted into the lumen of the colon. Mechanical and thermal behavioral tests were performed using an automated von Frey and Hargreaves device to evaluate somatic hyperalgesia. Colonic distension was performed using an automated distension device to evaluate visceral pain thresholds. All animals were tested 16weeks after TNBS treatment following complete resolution of the colitis.
Results: At 16weeks, 24% of the treated rats (18/75 rats) still exhibited evidence of visceral as well as somatic hypersensitivity compared to saline- and ethanol-treated rats.
Conclusion: Transient colonic inflammation leads to chronic visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in a subset of rats. These findings are similar to the subset of patients who develop chronic gastrointestinal symptoms following enteric infection.
Figures


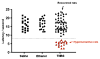
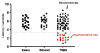
Similar articles
-
Visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in TNBS-induced colitis in rats.Dig Dis Sci. 2008 Feb;53(2):429-35. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9881-6. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2008. PMID: 17703363 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in a subset of hypersensitive rats by intracolonic lidocaine.Pain. 2008 Sep 30;139(1):218-224. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.04.002. Epub 2008 May 16. Pain. 2008. PMID: 18486344 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated H2 O2 levels in trinitrobenzene sulfate-induced colitis rats contributes to visceral hyperalgesia through interaction with the transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 cation channel.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jun;31(6):1147-53. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13226. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26574143
-
Visceral pain hypersensitivity in functional gastrointestinal disorders.Br Med Bull. 2009;91:123-36. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldp026. Epub 2009 Jul 19. Br Med Bull. 2009. PMID: 19620136 Review.
-
Visceral pain: the ins and outs, the ups and downs.Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012 Mar;6(1):17-26. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0b013e32834f6ec9. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012. PMID: 22246042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Auricular Allodynia is Associated With Worse Outcomes in Children With Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders Using Neurostimulation.Neuromodulation. 2025 Jul;28(5):840-846. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2025.02.011. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Neuromodulation. 2025. PMID: 40208134
-
NMDA receptor subunit expression and PAR2 receptor activation in colospinal afferent neurons (CANs) during inflammation induced visceral hypersensitivity.Mol Pain. 2009 Sep 22;5:54. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-54. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19772634 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Relieves Visceral Hypersensitivity via Balancing PAR2 and PAR4 in the Descending Pain Modulatory System of Goats.Brain Sci. 2023 Jun 7;13(6):922. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13060922. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37371401 Free PMC article.
-
Central and peripheral hypersensitivity in the irritable bowel syndrome.Pain. 2010 Mar;148(3):454-461. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.12.005. Epub 2010 Jan 13. Pain. 2010. PMID: 20074857 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of animal models of post-infectious/post-inflammatory irritable bowel syndrome.J Gastroenterol. 2011 Feb;46(2):164-74. doi: 10.1007/s00535-010-0321-6. Epub 2010 Sep 17. J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 20848144
References
-
- Adam B, Liebregts T, Gschossmann JM, Krippner C, Scholl F, Ruwe M, et al. Severity of mucosal inflammation as a predictor for alterations of visceral sensory function in a rat model. Pain. 2006;123:179–86. - PubMed
-
- Al Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ. A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:1276–85. - PubMed
-
- Bourdu S, Dapoigny M, Chapuy E, Artigue F, Vasson MP, Dechelotte P, et al. Rectal instillation of butyrate provides a novel clinically relevant model of noninflammatory colonic hypersensitivity in rats. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1996–2008. - PubMed
-
- Bouin M, Plourde V, Boivin M, Riberdy M, Lupien F, Laganiere M, et al. Rectal distention testing in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of pain sensory thresholds. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1771–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

