Structure of the FH2 domain of Daam1: implications for formin regulation of actin assembly
- PMID: 17482208
- PMCID: PMC1939941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.002
Structure of the FH2 domain of Daam1: implications for formin regulation of actin assembly
Abstract
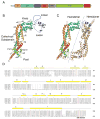
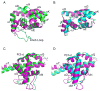
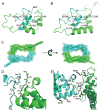
Daam1 (dishevelled-associated activator of morphogenesis-1) is a diaphanous-related formin first studied as a novel dishevelled binding protein and shown to be crucial for the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway in Xenopus. Daam1, like other formins, directs nucleation and elongation of new actin filaments using its conserved formin-homology-2 (FH2) domain. Here we report the crystal structure of a large C-terminal fragment of human Daam1 containing the FH2 domain. The structure, determined at 2.25 A resolution using the single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD) phasing method, reveals a "tethered dimer" architecture that is similar to that previously described for the FH2 domain of the yeast formin Bni1, which shares approximately 21% sequence identity with Daam1. Despite the overall similarity with the dimeric FH2 domain of Bni1 and with a truncated monomeric structure of mDia1, the Daam1 FH2 structure reveals a number of differences in secondary structure elements and in the "lasso/post" dimerization interface that may be functionally important. Most strikingly, the two halves of the crystallographic dimer pack together in a manner that occludes their actin binding surfaces. This "locked" conformation is stabilized by two novel, interacting beta-strands formed by the ends of the linkers that connect the two sides of the dimer. The Daam1 FH2 domain has weak actin assembly activity as compared with other mammalian formins, but mutations that disrupt the beta-strand lock increase activity about tenfold to a level comparable to other formins, suggesting that this occluded conformation may represent an auto-inhibited conformation of the Daam1 FH2 domain.
Figures


References
-
- Kovar DR. Molecular details of formin-mediated actin assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:11–7. - PubMed
-
- Higgs HN. Formin proteins: a domain-based approach. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:342–53. - PubMed
-
- Faix J, Grosse R. Staying in shape with formins. Dev Cell. 2006;10:693–706. - PubMed
-
- Goode BL, Eck MJ. Mechanism and Function of Formins in the Control of Actin Assembly. Annual Review of Biochemistry in press 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

