The two carboxylases of Corynebacterium glutamicum essential for fatty acid and mycolic acid synthesis
- PMID: 17483212
- PMCID: PMC1951862
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00254-07
The two carboxylases of Corynebacterium glutamicum essential for fatty acid and mycolic acid synthesis
Abstract
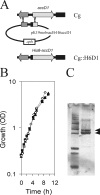
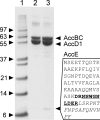
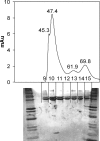
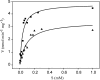
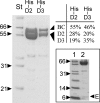
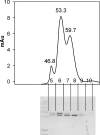
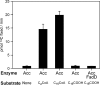
The suborder Corynebacterianeae comprises bacteria like Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Corynebacterium glutamicum, and these bacteria contain in addition to the linear fatty acids, unique alpha-branched beta-hydroxy fatty acids, called mycolic acids. Whereas acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase activity is required to provide malonyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis, a new type of carboxylase is apparently additionally present in these bacteria. It activates the alpha-carbon of a linear fatty acid by carboxylation, thus enabling its decarboxylative condensation with a second fatty acid to afford mycolic acid synthesis. We now show that the acetyl-CoA carboxylase of C. glutamicum consists of the biotinylated alpha-subunit AccBC, the beta-subunit AccD1, and the small peptide AccE of 8.9 kDa, forming an active complex of approximately 812,000 Da. The carboxylase involved in mycolic acid synthesis is made up of the two highly similar beta-subunits AccD2 and AccD3 and of AccBC and AccE, the latter two identical to the subunits of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase complex. Since AccD2 and AccD3 orthologues are present in all Corynebacterianeae, these polypeptides are vital for mycolic acid synthesis forming the unique hydrophobic outer layer of these bacteria, and we speculate that the two beta-subunits present serve to lend specificity to this unique large multienzyme complex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acyl-CoA carboxylases (accD2 and accD3), together with a unique polyketide synthase (Cg-pks), are key to mycolic acid biosynthesis in Corynebacterianeae such as Corynebacterium glutamicum and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 22;279(43):44847-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408648200. Epub 2004 Aug 11. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15308633
-
Acyl-CoA sensing by FasR to adjust fatty acid synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum.J Biotechnol. 2014 Dec 20;192 Pt A:96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.10.031. J Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25449109
-
The accD3 gene for mycolic acid biosynthesis as a target for improving fatty acid production by fatty acid-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum strains.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Dec;102(24):10603-10612. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9395-5. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30276713
-
Current knowledge on mycolic acids in Corynebacterium glutamicum and their relevance for biotechnological processes.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Dec;97(23):9923-30. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5265-3. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24113823 Review.
-
Regulation and structure of the heteromeric acetyl-CoA carboxylase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1861(9 Pt B):1207-1213. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27091637 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell envelope of corynebacteria: structure and influence on pathogenicity.ISRN Microbiol. 2013 Jan 21;2013:935736. doi: 10.1155/2013/935736. Print 2013. ISRN Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23724339 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of imbalances in sulfur assimilation and synthesis of sulfur-containing amino acids at the single-cell level.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Nov;79(21):6730-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01804-13. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23995919 Free PMC article.
-
Early evolution of the biotin-dependent carboxylase family.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 Aug 9;11:232. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-232. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21827699 Free PMC article.
-
Mycolic Acid Biosynthesis Genes in the Genome Sequence of Corynebacterium atypicum DSM 44849.Genome Announc. 2014 Aug 21;2(4):e00845-14. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00845-14. Genome Announc. 2014. PMID: 25146145 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the transcriptional regulator RamB (Rv0465c) in the control of the glyoxylate cycle in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Bacteriol. 2009 Dec;191(23):7260-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01009-09. Epub 2009 Sep 18. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19767422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alderwick, L. J., E. Radmacher, M. Seidel, R. Gande, P. G. Hitchen, H. R. Morris, A. Dell, H. Sahm, L. Eggeling, and G. S. Besra. 2005. Deletion of Cg-emb in Corynebacterianeae leads to a novel truncated cell wall arabinogalactan, whereas inactivation of Cg-ubiA results in an arabinan-deficient mutant with a cell wall galactan core. J. Biol. Chem. 280:32362-32371. - PubMed
-
- Bilder, P., S. Lightle, G. Bainbridge, J. Ohren, B. Finzel, F. Sun, S. Holley, L. Al-Kassim, C. Spessard, M. Melnick, M. Newcomer, and G. L. Waldrop. 2006. The structure of the carboxyltransferase component of acetyl-coA carboxylase reveals a zinc-binding motif unique to the bacterial enzyme. Biochemistry 45:1712-1722. - PubMed
-
- Cole, S. T., R. Brosch, J. Parkhill, T. Garnier, C. Churcher, D. Harris, S. V. Gordon, K. Eiglmeier, S. Gas, C. E. Barry III, F. Tekaia, K. K. Badcoc, D. Basham, D. Brown, T. Chillingworth, R. Connor, R. Davies, K. Devlin, T. Feltwell, S. Gentles, N. Hamlin, S. Holroyd, T. Hornsby, K. Jagels, A. Krogh, J. McLean, S. Moule, L. Murphy, K. Oliver, J. Osborne, M. A. Quail, M. A. Rajandream, J. Rogers, S. Rutter, K. Seeger, J. Skelton, R. Squares, S. Squares, J. E. Sulston, K. Taylor, S. Whitehead, and B. G. Barrell. 1998. Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 393:537-544. - PubMed
-
- Cole, S. T., K. Eiglmeier, J. Parkhill, K. D. James, N. R. Thomson, P. R. Wheeler, N. Honore, T. Garnier, C. Churcher, D. Harris, K. Mungall, D. Basham, D. Brown, T. Chillingworth, R. Connor, R. M. Davies, K. Devlin, S. Duthoy, T. Feltwell, A. Fraser, N. Hamlin, S. Holroyd, T. Hornsby, K. Jagels, C. Lacroix, J. Maclean, S. Moule, L. Murphy, K. Oliver, M. A. Quail, M. A. Rajandream, K. M. Rutherford, S. Rutter, K. Seeger, S. Simon, M. Simmonds, J. Skelton, R. Squares, S. Squares, K. Stevens, K. Taylor, S. Whitehead, J. R. Woodward, and B. G. Barrell. 2001. Massive gene decay in the leprosy bacillus. Nature 409:1007-1011. - PubMed
-
- Cronan, J. E. 2003. Bacterial membrane lipids: where do we stand? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57:203-224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

