A robust species tree for the alphaproteobacteria
- PMID: 17483224
- PMCID: PMC1913456
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00269-07
A robust species tree for the alphaproteobacteria
Abstract
The branching order and coherence of the alphaproteobacterial orders have not been well established, and not all studies have agreed that mitochondria arose from within the Rickettsiales. A species tree for 72 alphaproteobacteria was produced from a concatenation of alignments for 104 well-behaved protein families. Coherence was upheld for four of the five orders with current standing that were represented here by more than one species. However, the family Hyphomonadaceae was split from the other Rhodobacterales, forming an expanded group with Caulobacterales that also included Parvularcula. The three earliest-branching alphaproteobacterial orders were the Rickettsiales, followed by the Rhodospirillales and then the Sphingomonadales. The principal uncertainty is whether the expanded Caulobacterales group is more closely associated with the Rhodobacterales or the Rhizobiales. The mitochondrial branch was placed within the Rickettsiales as a sister to the combined Anaplasmataceae and Rickettsiaceae, all subtended by the Pelagibacter branch. Pelagibacter genes will serve as useful additions to the bacterial outgroup in future evolutionary studies of mitochondrial genes, including those that have transferred to the eukaryotic nucleus.
Figures
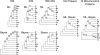

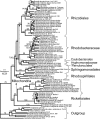


References
-
- Badger, J. H., J. A. Eisen, and N. L. Ward. 2005. Genomic analysis of Hyphomonas neptunium contradicts 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic analysis: implications for the taxonomy of the orders ′Rhodobacterales’ and Caulobacterales. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55:1021-1026. - PubMed
-
- Badger, J. H., T. R. Hoover, Y. V. Brun, R. M. Weiner, M. T. Laub, G. Alexandre, J. Mrazek, Q. Ren, I. T. Paulsen, K. E. Nelson, H. M. Khouri, D. Radune, J. Sosa, R. J. Dodson, S. A. Sullivan, M. J. Rosovitz, R. Madupu, L. M. Brinkac, A. S. Durkin, S. C. Daugherty, S. P. Kothari, M. G. Giglio, L. Zhou, D. H. Haft, J. D. Selengut, T. M. Davidsen, Q. Yang, N. Zafar, and N. L. Ward. 2006. Comparative genomic evidence for a close relationship between the dimorphic prosthecate bacteria Hyphomonas neptunium and Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 188:6841-6850. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batut, J., S. G. Andersson, and D. O'Callaghan. 2004. The evolution of chronic infection strategies in the alpha-proteobacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:933-945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

