Additive effects of SbcCD and PolX deficiencies in the in vivo repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Deinococcus radiodurans
- PMID: 17483232
- PMCID: PMC1913444
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00452-07
Additive effects of SbcCD and PolX deficiencies in the in vivo repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Deinococcus radiodurans
Abstract
Orthologs of proteins SbcD (Mre11) and SbcC (Rad50) exist in all kingdoms of life and are involved in a wide variety of DNA repair and maintenance functions, including homologous recombination and nonhomologous end joining. Here, we have inactivated the sbcC and/or sbcD genes of Deinococcus radiodurans, a highly radioresistant bacterium able to mend hundreds of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks (DSB). Mutants devoid of the SbcC and/or SbcD proteins displayed reduced survival and presented a delay in kinetics of DSB repair and cell division following gamma-irradiation. It has been recently reported that D. radiodurans DNA polymerase X (PolX) possesses a structure-modulated 3'-to-5' exonuclease activity reminiscent of specific nuclease activities displayed by the SbcCD complex from Escherichia coli. We constructed a double mutant devoid of SbcCD and PolX proteins. The double-mutant DeltasbcCD DeltapolX(Dr) (where Dr indicates D. radiodurans) bacteria are much more sensitive to gamma-irradiation than the single mutants, suggesting that the deinococcal SbcCD and PolX proteins may play important complementary roles in processing damaged DNA ends. We propose that they are part of a backup repair system acting to rescue cells containing DNA lesions that are excessively numerous or difficult to repair.
Figures


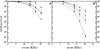

References
-
- Anderson, A. W., H. C. Nordon, R. F. Cain, G. Parrish, and G. Duggan. 1956. Studies on a radio-resistant micrococcus. I. Isolation, morphology, cultural characteristics, and resistance to gamma radiation. Food Technol. 10:575-578.
-
- Battista, J. R. 1997. Against all odds: the survival strategies of Deinococcus radiodurans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 51:203-224. - PubMed
-
- Battista, J. R., A. M. Earl, and M. J. Park. 1999. Why is Deinococcus radiodurans so resistant to ionizing radiation? Trends Microbiol. 7:362-365. - PubMed
-
- Blasius, M., I. Shevelev, E. Jolivet, S. Sommer, and U. Hubscher. 2006. DNA polymerase X from Deinococcus radiodurans possesses a structure-modulated 3′→5′ exonuclease activity involved in radioresistance. Mol. Microbiol. 60:165-176. - PubMed
-
- Bonacossa de Almeida, C., G. Coste, S. Sommer, and A. Bailone. 2002. Quantification of RecA protein in Deinococcus radiodurans reveals involvement of RecA, but not LexA, in its regulation. Mol. Genet. Genomics 268:28-41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

