Arabidopsis protein kinase PKS5 inhibits the plasma membrane H+ -ATPase by preventing interaction with 14-3-3 protein
- PMID: 17483306
- PMCID: PMC1913743
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.035626
Arabidopsis protein kinase PKS5 inhibits the plasma membrane H+ -ATPase by preventing interaction with 14-3-3 protein
Abstract
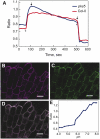
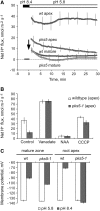
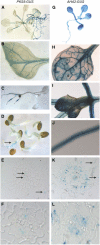
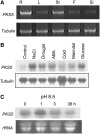
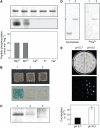
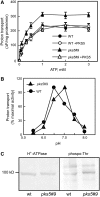
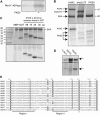
Regulation of the trans-plasma membrane pH gradient is an important part of plant responses to several hormonal and environmental cues, including auxin, blue light, and fungal elicitors. However, little is known about the signaling components that mediate this regulation. Here, we report that an Arabidopsis thaliana Ser/Thr protein kinase, PKS5, is a negative regulator of the plasma membrane proton pump (PM H+ -ATPase). Loss-of-function pks5 mutant plants are more tolerant of high external pH due to extrusion of protons to the extracellular space. PKS5 phosphorylates the PM H+ -ATPase AHA2 at a novel site, Ser-931, in the C-terminal regulatory domain. Phosphorylation at this site inhibits interaction between the PM H+ -ATPase and an activating 14-3-3 protein in a yeast expression system. We show that PKS5 interacts with the calcium binding protein SCaBP1 and that high external pH can trigger an increase in the concentration of cytosolic-free calcium. These results suggest that PKS5 is part of a calcium-signaling pathway mediating PM H+ -ATPase regulation.
Figures

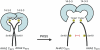
References
-
- Axelsen, K.B., Venema, K., Jahn, T., Baunsgaard, L., and Palmgren, M.G. (1999). Molecular dissection of the C-terminal regulatory domain of the plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase AHA2: Mapping of residues that when altered give rise to an activated enzyme. Biochemistry 38 7227–7234. - PubMed
-
- Babourina, O., Leonova, T., Shabala, S., and Newman, I. (2000). Effect of sudden salt stress on ion fluxes in intact wheat suspension cells. Ann. Bot. (Lond.) 85 759–767.
-
- Buch-Pedersen, M.J., Venema, K., Serrano, R., and Palmgren, M.G. (2000). Abolishment of proton pumping and accumulation in the E1P conformational state of a plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase by substitution of a conserved aspartyl residue in transmembrane segment 6. J. Biol. Chem. 275 39167–39173. - PubMed
-
- Cheng, N.H., Pittman, J.K., Zhu, J.K., and Hirschi, K.D. (2004). The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 279 2922–2926. - PubMed
-
- Demidchik, V., Bowen, H.C., Maathuis, F.J.M., Shabala, S.N., Tester, M.A., White, P.J., and Davies, J.M. (2002). Arabidopsis thaliana root non-selective cation channels mediate calcium uptake and are involved in growth. Plant J. 32 799–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

