Rational drug redesign to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy: imatinib moving target
- PMID: 17483313
- PMCID: PMC2769247
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0345
Rational drug redesign to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy: imatinib moving target
Erratum in
- Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 15;73(20):6375
Abstract
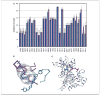
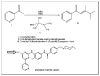
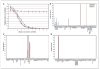
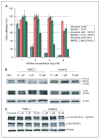
Protein kinases are central targets for drug-based cancer treatment. To avoid functional impairment, the cell develops mechanisms of drug resistance, primarily based on adaptive mutations. Redesigning a drug to target a drug-resistant mutant kinase constitutes a therapeutic challenge. We approach the problem by redesigning the anticancer drug imatinib guided by local changes in interfacial de-wetting propensities of the C-Kit kinase target introduced by an imatinib-resistant mutation. The ligand is redesigned by sculpting the shifting hydration patterns of the target. The association with the modified ligand overcomes the mutation-driven destabilization of the induced fit. Consequently, the redesigned drug inhibits both mutant and wild-type kinase. The modeling effort is validated through molecular dynamics, test tube kinetic assays of downstream phosphorylation activity, high-throughput bacteriophage-display kinase screening, cellular proliferation assays, and cellular immunoblots. The inhibitor redesign reported delineates a molecular engineering paradigm to impair routes for drug resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel tyrosine kinase switch is a mechanism of imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Oncogene. 2007 Jun 7;26(27):3909-19. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210173. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17325667
-
Resistance to c-KIT kinase inhibitors conferred by V654A mutation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):1159-66. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0641. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17363509
-
Sorafenib inhibits the imatinib-resistant KITT670I gatekeeper mutation in gastrointestinal stromal tumor.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 15;13(16):4874-81. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0484. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17699867
-
[Consensus on the medical treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2007 Nov;29(11):875-7. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18396652 Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;355:41-57. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_161. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22015552 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutation D816V alters the internal structure and dynamics of c-KIT receptor cytoplasmic region: implications for dimerization and activation mechanisms.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Jun;7(6):e1002068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002068. Epub 2011 Jun 16. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21698178 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding at the target-ligand interface leads the pathways of drug-designing.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 16;5(8):e12029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012029. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808434 Free PMC article.
-
Translational research in complex etiopathogenesis and therapy of hematological malignancies: the specific role of tyrosine kinases signaling and inhibition.Med Oncol. 2009 Dec;26(4):437-44. doi: 10.1007/s12032-008-9143-2. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Med Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19051068
-
Combined pharmacophore modeling, docking, and 3D-QSAR studies of PLK1 inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):8713-39. doi: 10.3390/ijms12128713. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22272100 Free PMC article.
-
c-Jun-NH2-kinase-1 inhibition leads to antitumor activity in ovarian cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 1;16(1):184-94. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1180. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20028751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Druker BJ. Circumventing resistance to kinase-inhibitor therapy. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2594–6. - PubMed
-
- Schittenhelm MM, Shiraga S, Schroeder A, et al. Dasatinib (BMS-354825), a dual SRC/ABL kinase inhibitor, inhibits the kinase activity of wild-type, juxtamem-brane, and activation loop mutant KIT isoforms associated with human malignancies. Cancer Res. 2006;66:473–81. - PubMed
-
- Shah N, Lee FY, Luo R, et al. (BMS-354825) inhibits KITD816V, an imatinib-resistant activating mutation that triggers neoplastic growth in most patients with systemic mastocytosis. Blood. 2006;108:286–91. - PubMed
-
- Attoub S, Rivat C, Rodrigues S, et al. The c-kit tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 for colorectal cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4879–83. - PubMed
-
- Mol CD, Dougan DR, Schneider TR, et al. Structural basis for the autoinhibition and STI-571 inhibition of c-Kit tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:31655–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

