Fine-tuning of translation termination efficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves two factors in close proximity to the exit tunnel of the ribosome
- PMID: 17483428
- PMCID: PMC2147991
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.070771
Fine-tuning of translation termination efficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves two factors in close proximity to the exit tunnel of the ribosome
Abstract
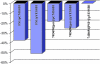
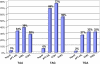
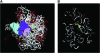
In eukaryotes, release factors 1 and 3 (eRF1 and eRF3) are recruited to promote translation termination when a stop codon on the mRNA enters at the ribosomal A-site. However, their overexpression increases termination efficiency only moderately, suggesting that other factors might be involved in the termination process. To determine such unknown components, we performed a genetic screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that identified genes increasing termination efficiency when overexpressed. For this purpose, we constructed a dedicated reporter strain in which a leaky stop codon is inserted into the chromosomal copy of the ade2 gene. Twenty-five antisuppressor candidates were identified and characterized for their impact on readthrough. Among them, SSB1 and snR18, two factors close to the exit tunnel of the ribosome, directed the strongest antisuppression effects when overexpressed, showing that they may be involved in fine-tuning of the translation termination level.
Figures



References
-
- Alkalaeva, E. Z., A. V. Pisarev, L. Y. Frolova, L. L. Kisselev and T. V. Pestova, 2006. In vitro reconstitution of eukaryotic translation reveals cooperativity between release factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell 125: 1125–1136. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann, R. P., L. E. Mizzen and W. J. Welch, 1990. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science 248: 850–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

