Bayesian multiple quantitative trait loci mapping for complex traits using markers of the entire genome
- PMID: 17483433
- PMCID: PMC1950652
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.064980
Bayesian multiple quantitative trait loci mapping for complex traits using markers of the entire genome
Abstract
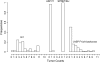
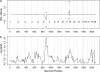
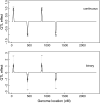
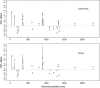
A Bayesian methodology has been developed for multiple quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping of complex binary traits that follow liability threshold models. Unlike most QTL mapping methods where only one or a few markers are used at a time, the proposed method utilizes all markers across the genome simultaneously. The outperformance of our Bayesian method over the traditional single-marker analysis and interval mapping has been illustrated via simulations and real data analysis to identify candidate loci associated with colorectal cancer.
Figures
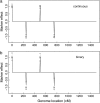
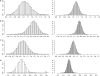
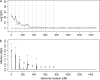
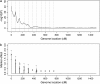
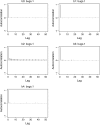
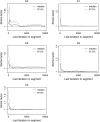
References
-
- Best, N. C., M. K. Cowles and S. K. Vines, 1995. CODA Manual Version 0.30. MRC Biostatistics Unit, Cambridge, UK.
-
- Carlborg, O., and L. Andersson, 2002. Use of randomization testing to detect multiple epistatic QTL. Genet. Res. 79: 175–184. - PubMed
-
- Falconer, D. S., 1965. The inheritance of liability to certain diseases, estimated from the incidence among relatives. Ann. Hum. Genet. 29: 51–71.
-
- Falconer, D. S., and T. F. C. Mackay, 1996. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, Ed. 4. Addison-Wesley, Boston.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

