The interplay between microRNAs and the neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase C controls proliferation of human neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 17483472
- PMCID: PMC1876554
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700071104
The interplay between microRNAs and the neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase C controls proliferation of human neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
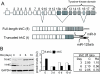
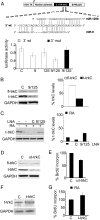
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are tiny noncoding RNAs whose function as modulators of gene expression is crucial for the proper control of cell growth and differentiation. Although the profile of miRNA expression has been defined for many different cellular systems, the elucidation of the regulatory networks in which they are involved is only just emerging. In this work, we identify a crucial role for three neuronal miRNAs (9, 125a, and 125b) in controlling human neuroblastoma cell proliferation. We show that these molecules act in an additive manner by repressing a common target, the truncated isoform of the neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase C, and we demonstrate that the down-regulation of this isoform is critical for regulating neuroblastoma cell growth. Consistently with their function, these miRNAs were found to be down-modulated in primary neuroblastoma tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Marked change in microRNA expression during neuronal differentiation of human teratocarcinoma NTera2D1 and mouse embryonal carcinoma P19 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Oct 19;362(2):360-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.189. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17716626
-
Down-regulation of hsa-miR-10a in chronic myeloid leukemia CD34+ cells increases USF2-mediated cell growth.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Dec;6(12):1830-40. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0167. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19074828
-
MicroRNAs and their emerging roles in immunology.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Nov;1143:226-39. doi: 10.1196/annals.1443.009. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 19076353 Review.
-
Muscling through the microRNA world.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008 Feb;233(2):131-8. doi: 10.3181/0709-MR-237. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008. PMID: 18222968 Review.
-
MicroRNA-34a inhibits uveal melanoma cell proliferation and migration through downregulation of c-Met.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Apr;50(4):1559-65. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2681. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19029026
Cited by
-
Changes in brain MicroRNAs contribute to cholinergic stress reactions.J Mol Neurosci. 2010 Jan;40(1-2):47-55. doi: 10.1007/s12031-009-9252-1. Epub 2009 Aug 27. J Mol Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 19711202 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics, nervous system tumors, and cancer stem cells.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Sep 13;3(3):3525-56. doi: 10.3390/cancers3033525. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212967 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA and cancer.Mol Oncol. 2012 Dec;6(6):590-610. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Mol Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23102669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-125a-3p regulates glioma apoptosis and invasion by regulating Nrg1.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 5;10(1):e0116759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116759. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25560389 Free PMC article.
-
miR-15a-5p, miR-15b-5p, and miR-16-5p inhibit tumor progression by directly targeting MYCN in neuroblastoma.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jan;14(1):180-196. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12588. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31637848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Smirnova L, Grafe A, Seiler A, Schumacher S, Nitsch R, Wulczyn FG. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:1469–1477. - PubMed
-
- Giraldez AJ, Cinalli RM, Glasner ME, Enright AJ, Thomson JM, Baskerville S, Hammond SM, Bartel DP, Schier AF. Science. 2005;308:833–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

