Synthesis of beta(2)-microglobulin-free, disulphide-linked HLA-G5 homodimers in human placental villous cytotrophoblast cells
- PMID: 17484767
- PMCID: PMC2266009
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02623.x
Synthesis of beta(2)-microglobulin-free, disulphide-linked HLA-G5 homodimers in human placental villous cytotrophoblast cells
Abstract
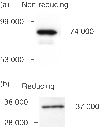
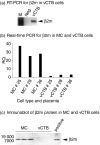
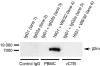
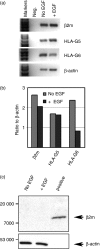
Human leucocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) is a natural immunosuppressant produced in human placentas that binds differently to the inhibitory leucocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors LILRB1 (ILT2) and LILRB2 (ILT4) according to its biochemical structure. To predict the binding functions of the HLA-G5 soluble isoform synthesized in placental villous cytotrophoblast (vCTB) cells, we investigated structural features of this protein. Biochemical and immunological studies showed that vCTB cell HLA-G5 heavy (H)-chain proteins are disulphide-bonded homodimers unassociated with beta(2)-microglobulin (beta2m) light-chain proteins. Although comparatively low levels of beta2m messenger RNA (mRNA) were identified by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, immunoprecipitation studies failed to detect beta2m protein even when specific mRNA was doubled by transduction of a lentivirus-beta2m complementary DNA into vCTB cells. No abnormalities were identified in the translational start codon of vCTB cell beta2m mRNA and differentiation into syncytium did not promote beta2m synthesis. The failure of vCTB cells to exhibit beta2m in vitro was paralleled by a lack of detectable beta2m in vCTB cells in vivo. Lack of the beta2m protein could be the result of low levels of beta2m transcripts or of as yet unidentified translational defects. Experiments with recombinant ectodomains of LILRB indicate that beta2m-free HLA-G binds strongly to LILRB2, a receptor that is expressed by macrophages. This potentially immunosuppressive cell type is abundant in the pregnant uterus. Thus, our findings are consistent with the postulate that the natural beta2m-free homodimeric form of HLA-G5 synthesized in primary vCTB cells could comprise a particularly effective tolerogenic molecule at the maternal-fetal interface.
Figures

References
-
- Hunt JS, Petroff MG, McIntire RH, Ober C. HLA-G and immune tolerance in pregnancy. FASEB J. 2005;19:681–93. - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer KA, Rebmann V, Passler M, van der Ven K, van der Ven H, Grosse-Wilde H. Soluble HLA levels in early pregnancy after in vitro fertilization. Hum Immunol. 2000;61:559–64. - PubMed
-
- Yie S, Balakier H, Motamedi G, Librach C. Secretion of human leukocyte antigen-G by human embryos is associated with a higher in vitro fertilization pregnancy rate. Fert Steril. 2005;83:30–6. - PubMed
-
- Aldrich CL, Stephenson MD, Karrison T, et al. HLA-G genotypes and pregnancy outcome in couples with unexplained recurrent miscarriage. Mol Hum Reprod. 2001;7:1162–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

